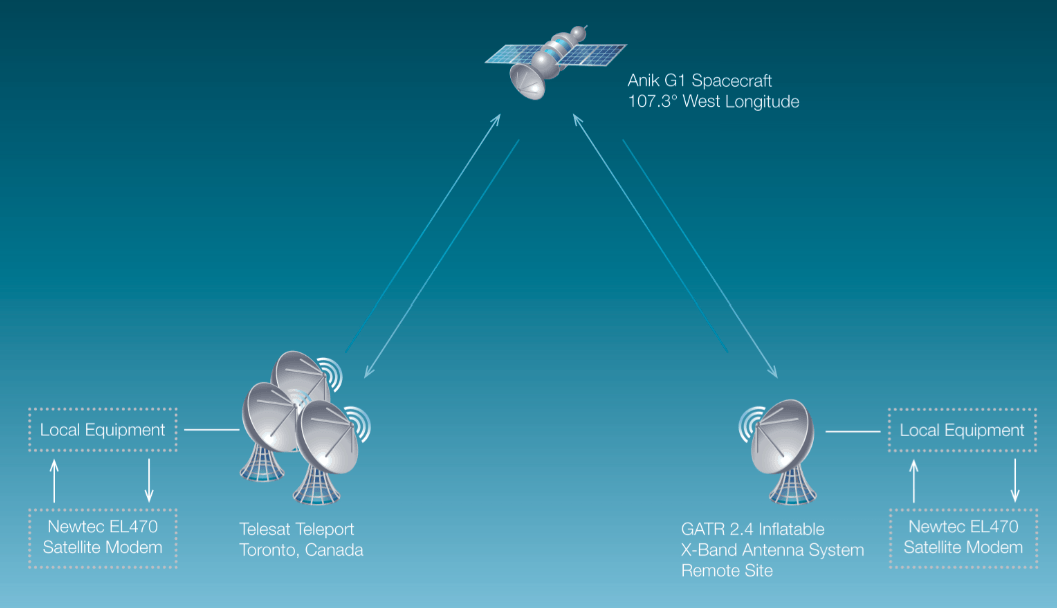
In this article we will cover satellite based hacking attack which has been used by hacking groups since many years. This attack will provide you complete anonymity and thus it will be very difficult of the digital forensics experts to trace you. In the last article about hacking satellite traffic, we covered the following topics.
- Setting up satellite dish.
- Different satellites and corresponding frequencies.
- Different software’s to scan satellite frequencies.
- Ways to intercept downlink satellite traffic.
- How to get free satellite internet and television and basic hacking attacks.
With the help of software like DVB Snoop and Wireshark we can intercept satellite communications and take dump of data as communication is not encrypted explains Mike Steven expert of cyber security training. After following the steps mentioned in previous article, we will set up satellite dish pointing to the specific satellite that is broadcasting the traffic. As we know the packets are unencrypted, we will use DVB- Snoop along to Wireshark to snoop the traffic. Once an IP address that is routed through the satellite’s downstream link is identified, we can start listening for packets coming from the Internet to this specific IP. As we can view the packets, we can do TCP hijacking attack easily according to expert from a cyber security company
What is Satellite TCP hijacking Attack?
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a very important protocol of the transport layer.TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, which means a connection is made and maintained until the application programs at each end have finished communication. This protocol determines how to divide application data into packets that network can deliver. It also communicates with the network layer and manages flow control. The TCP stack divides the file into packets, numbers them and then forwards them individually to the IP layer for delivery. It also manages retransmission and acknowledgement of packets says cyber security organization expert. In the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) communication model, TCP covers parts of Layer 4, the Transport Layer, and parts of Layer 5, the Session Layer. TCP processes packets by sequence number as they are received, and it puts out-of-order packets back into place. The TCP protocol is the only protocol from the TCP/IP protocol family that supports additional packet, connection identification and authentication mechanisms. That explains why application level protocols, such as SMTP, FTP, etc use TCP to gain remote access to other hosts. For defining packets, the TCP header consists of two 32-bit fields that are used as packet counters. They are named Sequence Number and Acknowledgment Number. Another field, named Control Bit, is 6 bits long, and it carries the following command flags. It’s very important to cover logic of these flag during any cyber security training.
URG: Urgent Flag
ACK: Acknowledgment Flag
PSH: Push Flag
RST: Reset Flag
SYN: Synchronize sequence numbers Flag
FIN: No more data from sender flag
During TCP hijacking attack the hacker takes over communication session between different users by masquerading as the authorized user. Once the user’s session details have been accessed the hacker can masquerade as that user and do anything the user is authorized to do on the network.
Satellite TCP hijacking methods
There are different satellites TCP hijacking methods explains Dave Taylor, digital forensics expert and some of them are:
IP Spoofing
IP spoofing is a technique used to gain unauthorized access of communication, where the messages are sent by the hijacker to a computer with an IP address of a trusted host. When the hijacker has successfully spoofed an IP address, he/she determines the next sequence number that the satellite expects and injects the forget packet with the same into the TCP session before the client can respond. Thus creates an unsynchronized state. The sequence and ACK numbers are no longer synchronized between client and satellite and hijacker take advantage of this situation to establish connection as trusted user explains cyber security company expert.
Blind Hijacking
When the source routing is disabled and hijacker can’t see the satellite response. The hijacker uses blind hijacking where the hijacker injects his malicious data into intercepted communications in a TCP session. Thus the word “blind” because the hijacker can send the data or commands, but cannot see the response. The hijacker basically guesses the responses of the client and satellite.
Man in the Middle attack (Packet sniffing)
According cyber security training professor, this is a technique which involves using a packet sniffer to intercept the communication between the client and satellite. With all the data between the hosts flowing through the hijacker’s sniffer, he is free to modify the content of the packets. This technique is to get the packets to be routed through the hijacker’s host.
For hijacking satellite communication hackers normally use combination of man in the middle attack and IP spoofing. A normal TCP communication has a 3 way handshake using SYN packet from user to satellite, then SYN + ACK from satellite to user and finally ACK from user to satellite.

During a TCP hijacking attack, the hacker intercepts the communication and sends a RST packet to user and starts communicating with the satellite with the spoofed IP address of the user.
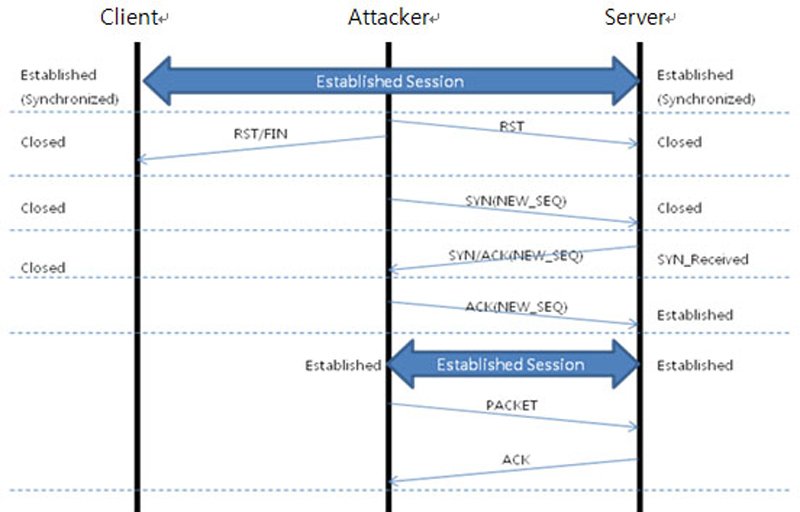
How to do Satellite TCP Hijacking
You can use following to tools to do Satellite TCP Hijacking:
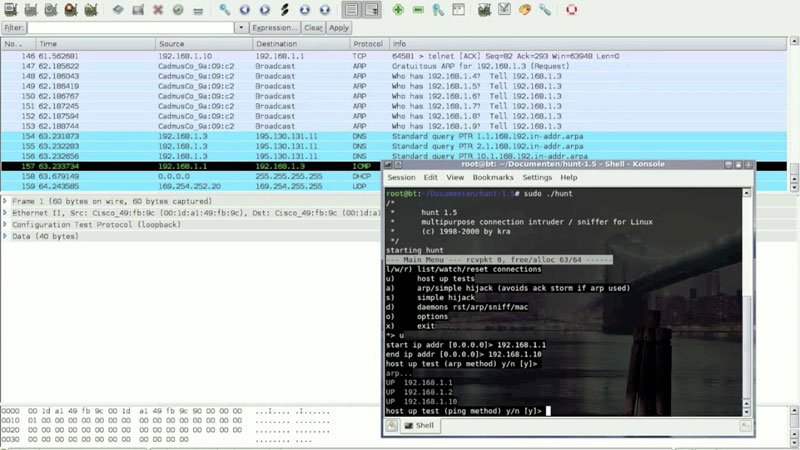
Hunt
Hunt (Linux binary distribution) is a program for intruding into a TCP connection, watching it and resetting it according to cyber security training professor.
1) With hunt we can do connection management and detect an ongoing connection. It allows normal active hijacking with the detection of the ACK, APR spoof and synchronization of the client with the satellite after hijacking.
2) Reset daemon for automatic connection resetting and act as demon relay for ARP spoof. It allows searching strings in traffic and collecting MAC addresses.
3) It acts as a DNS host resolving and extensible packet engine for watching TCP, UDP, ICMP and ARP traffic.
Shijack
Shijack is a TCP connection-hijacking tool for Linux, FreeBSD, and Solaris. The tool requires Libnet. It’s an open source code and can be use to take control of the TCP Session.

Scapy
Scapy is a powerful interactive packet manipulation tool written in Python, and the best part is that it can also be utilized as a library in Python programs, which provides the pentester the ability to create his/her own tool based on the requirement. It allows us to sniff, create, send and slice packets for hacking and digital forensics analysis.
Juggernaut
Juggernaut is basically a network sniffer that can also be used to hijack TCP sessions. It runs on Linux and has a Trinux module as well. Juggernaut can be activated to watch all network traffic on the local network, or can be set to listen for a special “token”. By doing so, this tool can be used to historically capture certain types of traffic by simply leaving the tool running for a few days, and then the attacker just has to pick up the log file that contains the recorded traffic.

In the next article we will cover more about advance hacking attacks involving satellites, you can also learn this during advanced ethical hacking and cyber security training of International Institute of Cyber Security. This article is for educational purposes only.
Read more about this:
https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2015/10/05/how-to-intercept-satellite-communications-easily/
Source:https://www.iicybersecurity.com/attack-satellite-communications.html

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.











