Critical flaws that affect many ThinkBook, IdeaPad, and Yoga laptop models have been resolved by Lenovo and may have allowed an attacker to disable UEFI Secure Boot.
Researchers from ESET found these flaws in drivers in several Lenovo systems and informed the computer maker of their discovery.
ESET published a link to a Twitter thread by Nikolaj Schlej explaining why UEFI firmware developers should not utilize NVRAM as trusted storage and claims that the vulnerabilities may be easily exploited by simply establishing specific NVRAM variables.
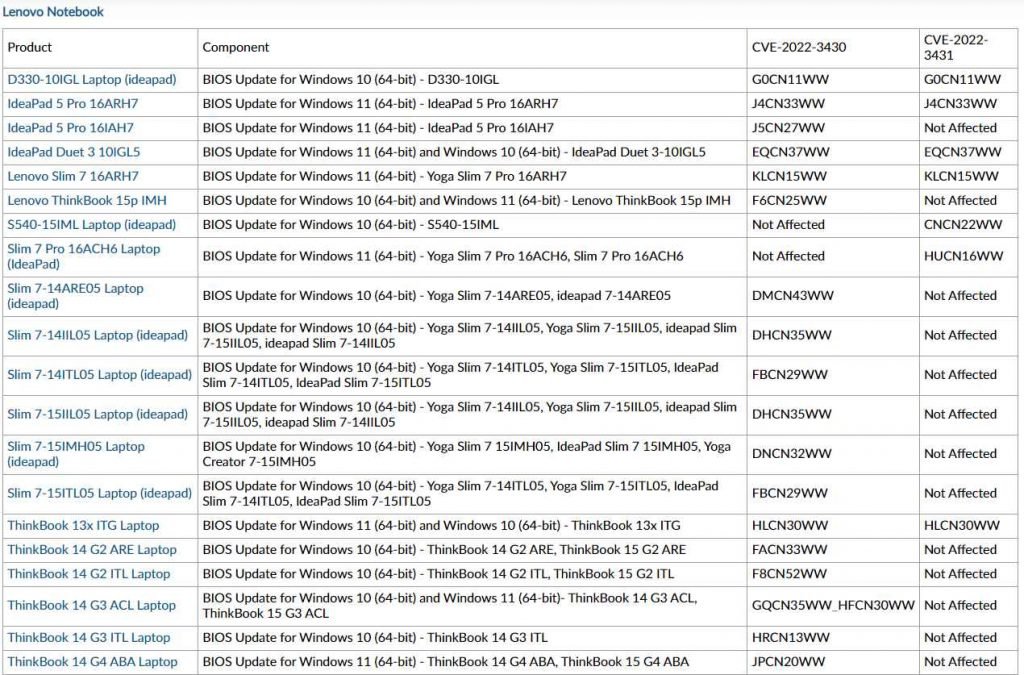
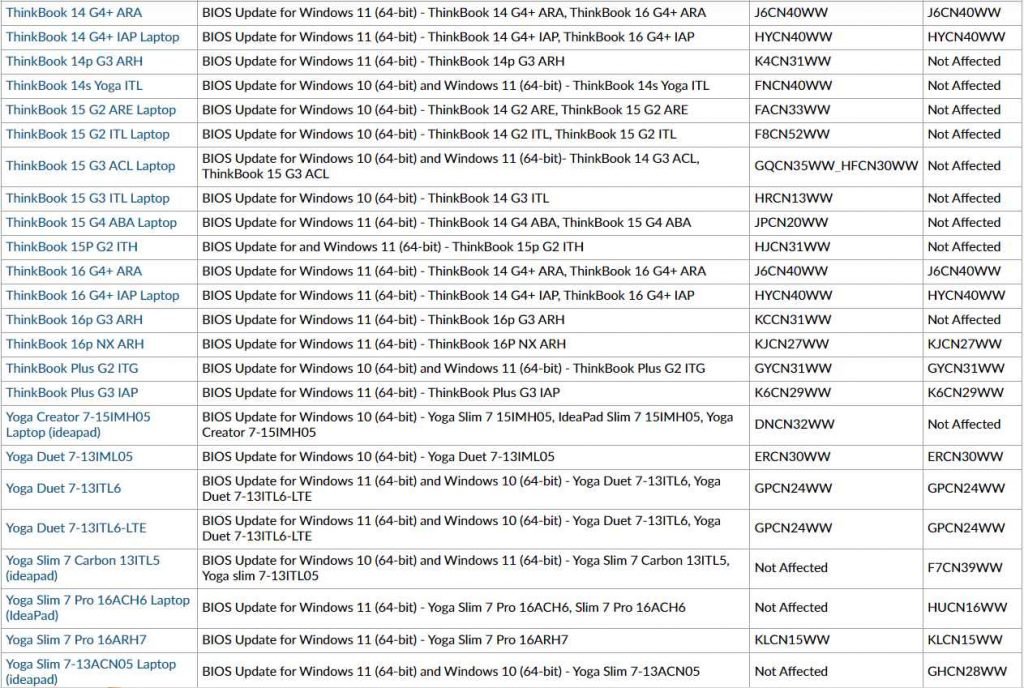
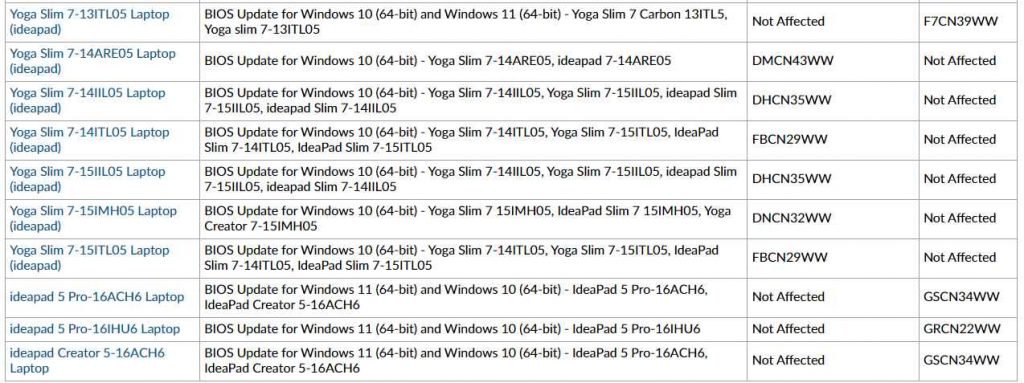
The Lenovo Notebook BIOS has been found to have the following vulnerabilities.
CVE-2022-3430
A possible flaw in the WMI Setup driver on a few consumer-grade Lenovo Notebook devices might give an attacker with administrative rights the ability to change the secure boot settings by altering an NVRAM variable.
CVE-2022-3431
A possible flaw in a driver that was inadvertently left enabled during manufacture on some consumer Lenovo Notebook devices might give an attacker with elevated privileges access to change the secure boot option by altering an NVRAM variable.
CVE-2022-3432
A possible flaw in a driver installed on the Ideapad Y700-14ISK during manufacture that was inadvertently left on might give an attacker with elevated privileges access to change the secure boot settings by altering an NVRAM variable.
Affected models
Strategy for Mitigation
Update system firmware to the version (or newer) specified for your model in the product Impact section to address CVE-2022-3430 and CVE-2022-3431.
The Ideapad Y700-14ISK has reached the end of development support for CVE-2022-3432, and no solutions will be made available. Customers are advised by Lenovo to use secure computing techniques, such as active system lifecycle management.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.











