In their latest investigation, Sophos security team detailed how a group of threat actors managed to steal millions of dollars from users of Tinder, Grindr, Facebook Dating, Bumble and other dating apps in their iOS version. Apparently, the attackers chose a potential victim and then gained their trust to make them download fraudulent cryptocurrency investment applications.
To distribute the malicious apps, the scam operators managed to manipulate Developer Enterprise and Enterprise/Corporate Signature, two Apple app developer programs. The apps used by the hackers posed as tools from Binance and other cryptocurrency exchange platforms.
The scam is managed remotely by abuse of Apple’s legitimate tools.
The malicious operation, identified as CryptoRom, allowed threat actors to steal at least $1.4 million USD from users of the aforementioned apps in the United States and some European Union countries, although it is not ruled out that they have also attacked users in Asia.
Jagadeesh Chandraiah, a researcher at Sophos, mentions that virtually every stage of this fraudulent scheme depends on a successful social engineering campaign, indicating that scammers are adept at interacting with potential targets and can easily gain anyone’s trust.
“Attackers start by creating fake profiles on popular dating apps. After contacting a user and gaining their trust, the attackers will propose to take the conversation to an instant messaging platform where they will try to persuade the target to install a cryptocurrency exchange application and invest money in the platform.
These platforms of dubious legitimacy are characterized by showing users a good initial performance, making the user lower their guard. Eventually, the funds stored in the victims’ accounts will simply disappear without explanation.
Experts believe that it all starts in dating apps because through these platforms it is easier to form a bond of trust with potential victims. In addition, the proposal to start a conversation through WhatsApp or Facebook Messenger can be taken as a good sign by legitimate users of dating apps.
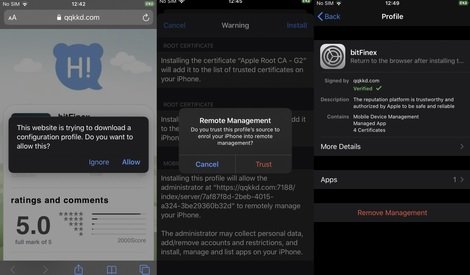
Moreover, experts mention that the cryptocurrency scam might not be the only target of threat actors, as abuse of developer tools at Apple could allow improper access to iPhone devices. It is worth mentioning that these systems were created so that developers could test apps for iOS before sending them to the App Store.
According to Chandraiah, the abuse of these functionalities would allow the deployment of attacks to large groups of iPhone users, creating the possibility of remotely controlling the compromised devices, in addition to collecting confidential information and installing other malicious apps.
Although its origin has already been traced, the campaign is still active, so users of dating apps are advised not to take their interactions to other platforms unless they can verify the identity of the other person. In addition, it is recommended not to install applications from unofficial platforms and in case they wish to invest in cryptocurrency, it is best to seek out a specialized advisor to reduce the risk of investing in an illegitimate platform.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.











