Every week there are multiple reports of security threats that could affect social media users, mainly Facebook. This time, information security awareness experts from CyberNews revealed an active scam that abuses some security flaws on PayPal and Facebook.
Exploiting these flaws, threat actors are stealing an average of $1.5 million a month. To do this, they just need to convince Facebook users to send to hacker-controlled addresses.
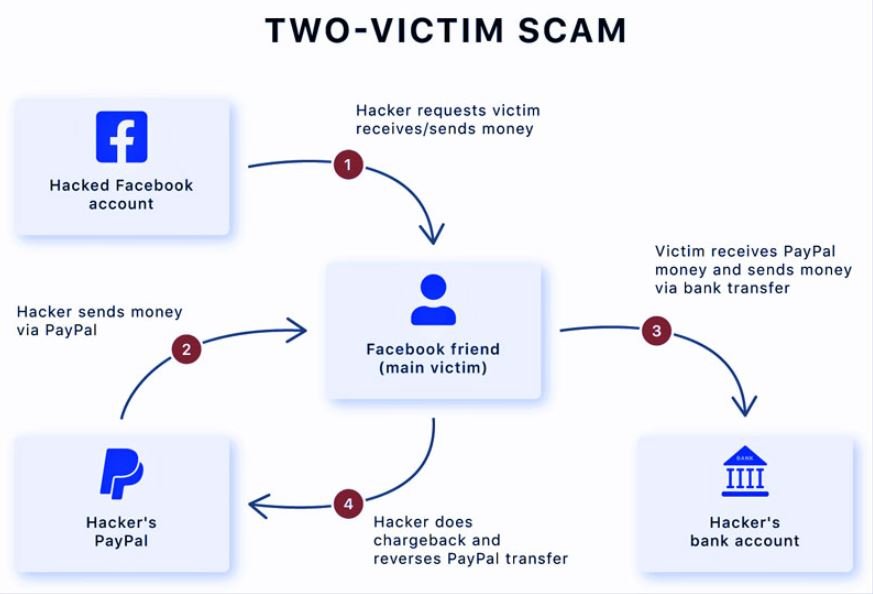
According to information security awareness experts, the attack can be divided into four different stages:
- A hacker logs into a Facebook or Messenger account and starts sending messages to the real account owner’s friends to ask for help with a problem in their PayPal account, or to offer the sale of a product. Hackers use phishing to get the user’s login credentials
- The cybercriminal asks the victim’s friends if they could receive money in their PayPal accounts and forward the same amount to the bank account operated by the hackers
- When the friend receives the money in their PayPal account, they send it by bank transfer to the hacker’s account
- Threat actors use the PayPal chargeback feature, which reverts the money sent to the friend in the first place, and the friend loses that money
The attacks appear to originate in various parts of the US, Russia and the United Kingdom, and the main targets are British Facebook users.
Information security awareness experts contacted some informants in the malicious hacking community, who revealed that the cybercriminals behind this campaign employ some simple security gaps present on PayPal, Facebook and even in some banks.
Recently, CyberNews also revealed the finding of six critical vulnerabilities in the PayPal payment system that could be exploited by malicious hackers to easily access users’ accounts; So far, PayPal has not yet corrected all reported bugs.
In this regard, a representative of the payment system mentioned: “Security risks are a very serious matter for us; we employ advanced risk and fraud management tools to protect our customers and their payments”.
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks you can access the Website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.










