Cybercriminals are now peddling a new piece of malicious software for Android called “Hook,” which boasts the ability to remotely take control of mobile devices in real-time via VNC (virtual network computing). The malicious software is promoted as having been “built from scratch.” This is questionable due to the fact that the bulk of the code base is still the one that was created by Ermac. This code base includes some instructions in Russian that show unwarranted anxiety about the world.
It is true that this iteration of the malware includes quite a few changes compared to its predecessor; nonetheless, it is quite evident that this is only an upgrade and enhancement of the earlier versions of Ermac. It is likely that the criminals, adopting a tactic that is commonly used in marketing strategies, made the decision to launch a new brand with their most recent product rather than keeping the existing one, which was associated primarily with activities pertaining to cryptowallets and the exfiltration of personally identifiable information (PII). This is a very plausible explanation for the events that took place. Following a successful installation and configuration of the malware, the bot will attempt to communicate with its C2 server using standard HTTP traffic.
In its connection with the C2 Server, Hook employs the same same encryption methods that Ermac makes use of. The information is first encoded in Base64 before being encrypted using AES-256-CBC with a key that has been hardcoded. In addition to the HTTP traffic that was used in the earlier Ermac versions, this new form of the malware now utilizes WebSocket communication. This is a change that was made as part of the modification process. The implementation is dependent on Socket.IO, which is an implementation over HTTP and WebSocket that allows real-time communication in both directions between web clients and servers. This communication may take place in real time. This is the channel over which the bot registers itself with its server, transmits a list of programs that are currently installed on the device, and downloads a list of targets.
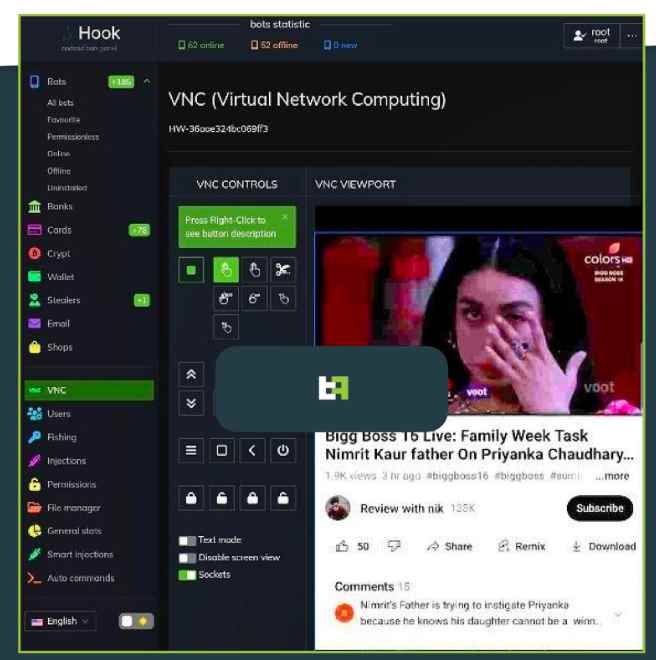
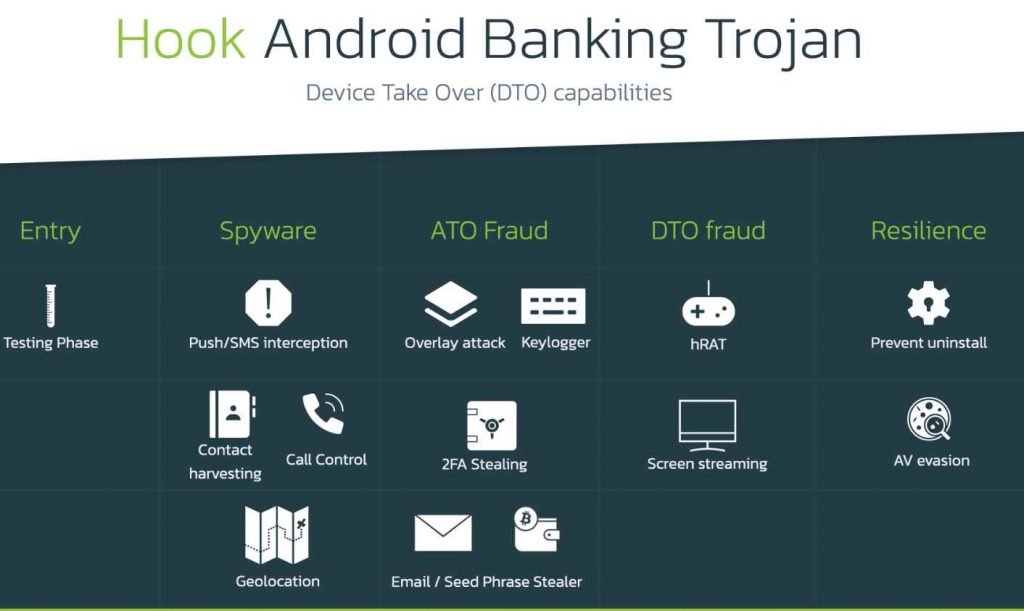
The most significant improvement in terms of capabilities is provided by a component known as VNC, which stands for virtual network computing. Virtual Network Computing, sometimes known as VNC, is a specialized version of a program that allows users to share their screens and exercise remote control over their devices. However, threat actors have been using this phrase to denote any kind of functionality that may be found in a Remote Access Tool (RAT). In the instance of Hook, this is accomplished by interacting with the many UI components that are necessary to carry out a broad variety of tasks via the use of the Accessibility Services.
Hook is now able to join the ranks of malware families that are capable of performing full DTO and completing a full fraud chain without the need of any extra channels, beginning with the exfiltration of personally identifiable information and continuing all the way through the transaction. The fact that fraud scoring systems have a far more difficult time identifying this sort of activity is the primary selling point for Android bankers.
The malicious software is able to simulate a broad variety of user actions on the device, including as clicking, filling in text areas, and executing gestures. This is the list of new commands that are associated with the RAT features that have been reported.
Similar to those of earlier iterations of Ermac, the target list is quite comprehensive and comprises establishments from all over the globe.
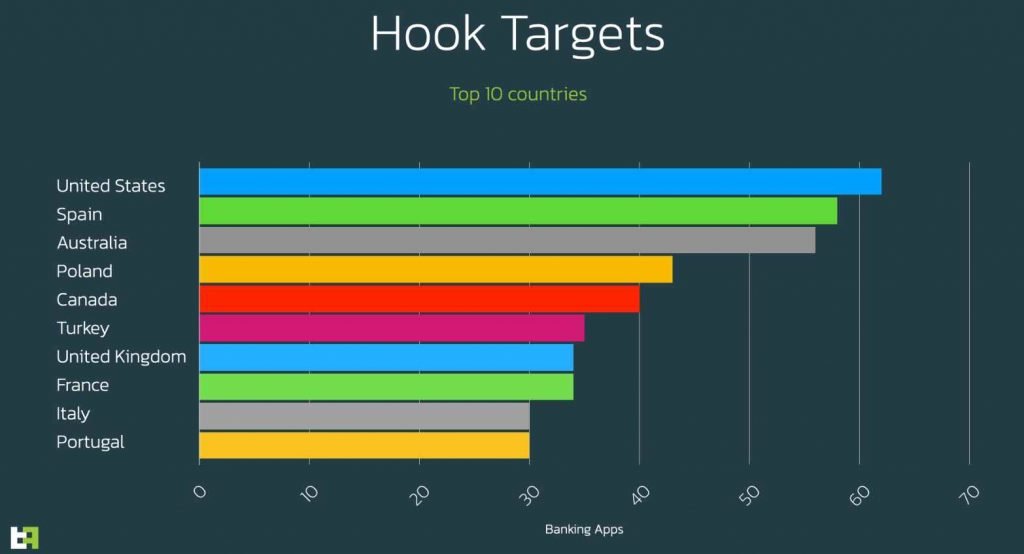
The actor makes a guarantee to his purchasers of more than a hundred targets, the vast majority of them are the same objectives that were available in earlier editions of Ermac. On the other hand, this updated version includes hundreds of additional targets, some of which are social applications and others of which are financial applications. New targets include those who have been banned from entering the country from South America, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
You may obtain a quick review of the areas that Hook focuses on the most by looking at the following:
The recent events surrounding Hook, the most recent member of the Ermac family of viruses, are pointing in a very specific path. Hook is now a member of the very hazardous class of malware that is able to carry out a whole attack chain, beginning with infection and ending with fraudulent transaction. In addition to this, it comes equipped with new features that are typical of spyware. These features make it possible for criminals to monitor and spy on the device, giving them complete visibility not only into the victim’s financial information, but also into their messaging, geolocation, and control over the files that are stored on the phone. As was previously mentioned, the Ermac malware family was one of the most widely distributed families in 2022. Now, with the release of its most recent development, Hook, ThreatFabric anticipates that Ermac will make the final quality leap and join Hydra and ExobotCompact/Octo on the podium of Android Bankers that are available for rent.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.











