A recently discovered security flaw in the Linux kernel might be exploited locally by an attacker to get elevated privileges on susceptible computers and run malicious script on such systems.
The vulnerability, which has been assigned the tracking number CVE-2022-4139 and received a CVSS score of 7.0, affects impacted Linux kernel stable branches (all of which were released after 5.4) and is the consequence of a security vulnerability in the Linux kernel’s GPU i915 kernel driver.
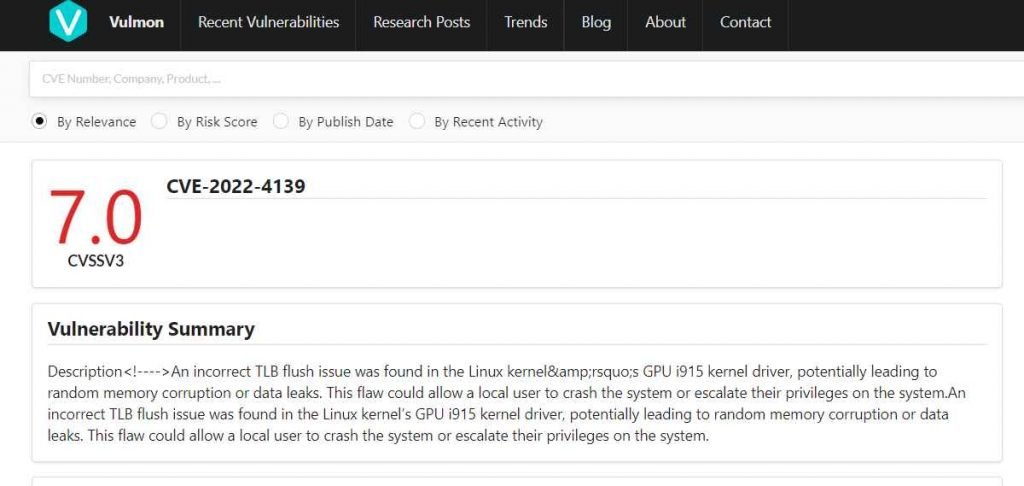
In order for attackers to properly exploit this vulnerability, they require access to the system that is being targeted so that they can execute their exploit, which either results in the getting of sensitive information or the cause of random memory corruption.
CVE-2022-4139 affects all Intel integrated and discrete GPUs Gen12, including Tiger Lake, Rocket Lake, Alder Lake, DG1, Raptor Lake, DG2, Arctic Sound, and Meteor Lake. This flaw might allow remote attackers to take control of an affected system.
Despite the fact that a researcher has backported the fixes to all impacted stable branches in order to solve the problem, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian have not yet adopted the improvements and are consequently susceptible to the attacks. Apply the patch and rebuild the kernel on your own if you are an experienced Linux user. Alternately, you might wait for the next kernel upgrade that is made available by your distribution provider and then implement it as quickly as you can.
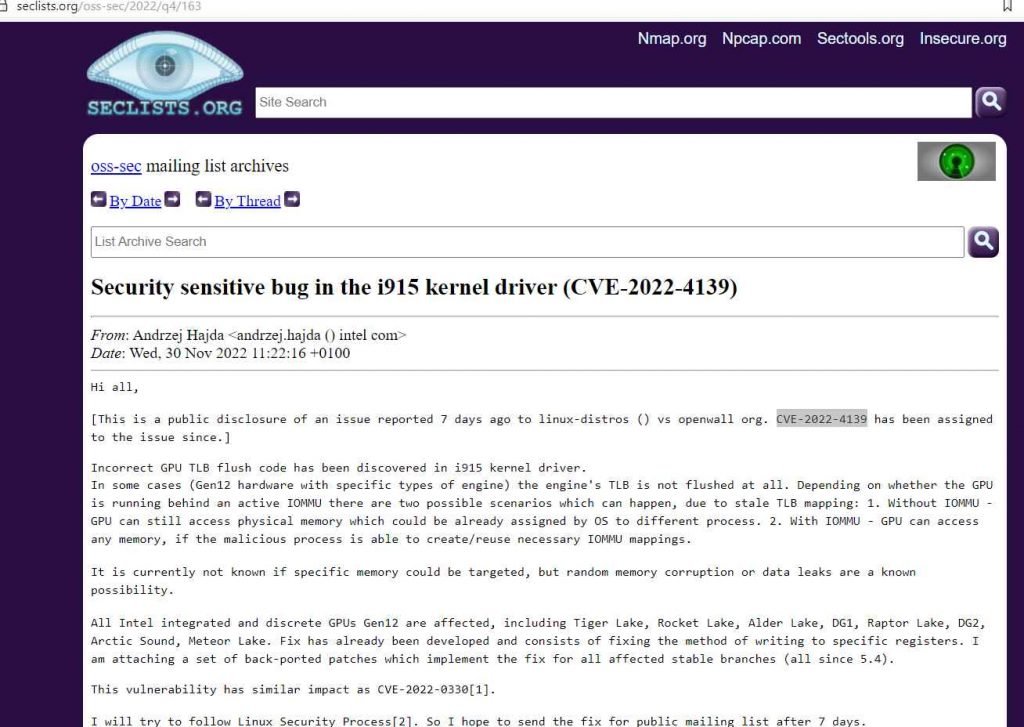
The researcher claims that
In some circumstances (Gen12 hardware equipped with certain varieties of engine), the TLB of the engine is not drained at all. Due to stale TLB mapping, there are two different outcomes that might occur depending on whether or not the GPU is operating in front of an active IOMMU. These outcomes are as follows: 1. Even without IOMMU, the GPU is still able to access physical memory, which the operating system may have previously allocated to other processes. 2. If IOMMU is present, the GPU will be able to access any memory, provided that the malicious process is able to construct and reuse the appropriate IOMMU mappings.
At this time, it is unknown whether or not particular memory might be targeted; nonetheless, random memory corruption or data breaches are known to be possible outcomes.
All Intel integrated and discrete GPUs Gen12, such as Tiger Lake, Rocket Lake, Alder Lake, DG1, Raptor Lake, DG2, Arctic Sound, and Meteor Lake, are impacted by this issue. Fix has already been created and comprises of correcting the way of writing to certain registers in the computer.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.











