Oracle Access Manager (OAM) contains a pre-authentication RCE vulnerability (CVE-2021-35587) that was fixed in January 2022. However, the vulnerability is still being exploited by adversaries in the wild, as confirmed by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, which added the vulnerability to its Catalog. CVE-2021-35587 has been added to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog by CISA, and all federal agencies have been asked to remediate it by December 19 at the latest. In addition, CVE-2022-4135, the eighth Chrome zero-day vulnerability fixed by Google so far this year, has been added to the database that the organization maintains.

Even though CISA only raised the warning this week, data gathered by a business that specializes in threat intelligence suggests that efforts to exploit the weakness in the wild began in September, with activity heating up in October and November. Greynoise has so far detected exploitation attempts originating from more than a dozen separate IP addresses. After Jang and Peterjson revealed a portion of their exploit for CVE-2021-35587 in March 2022, many proof-of-concept exploits for the vulnerability have since been published on GitHub.
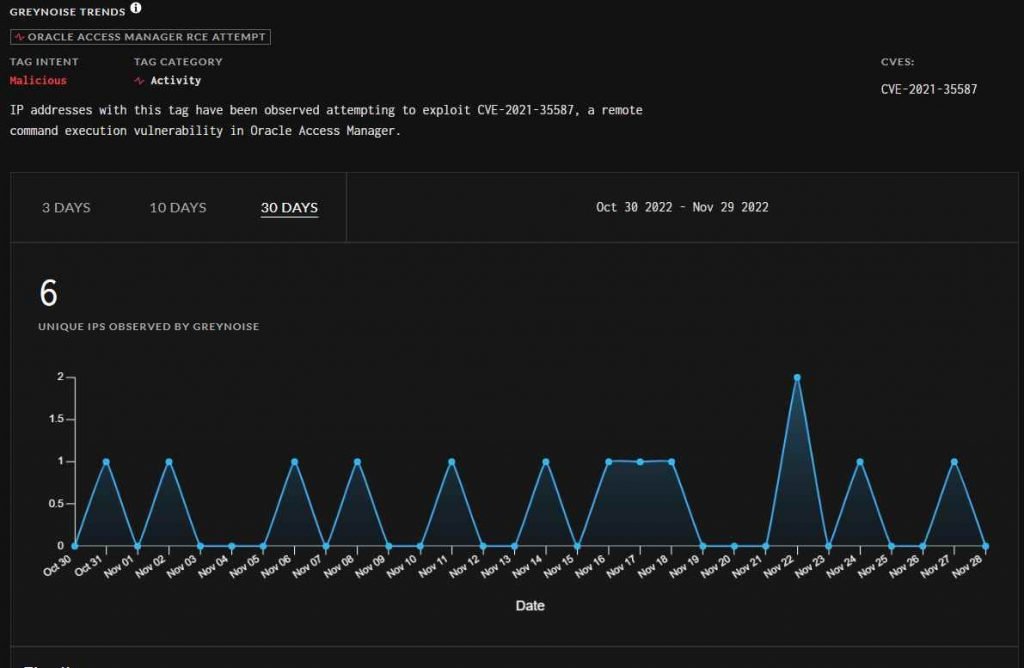
However, according to CISA, successful exploitation efforts have now been identified. Regrettably, the agency has not supplied any new information or details on these attacks (s).
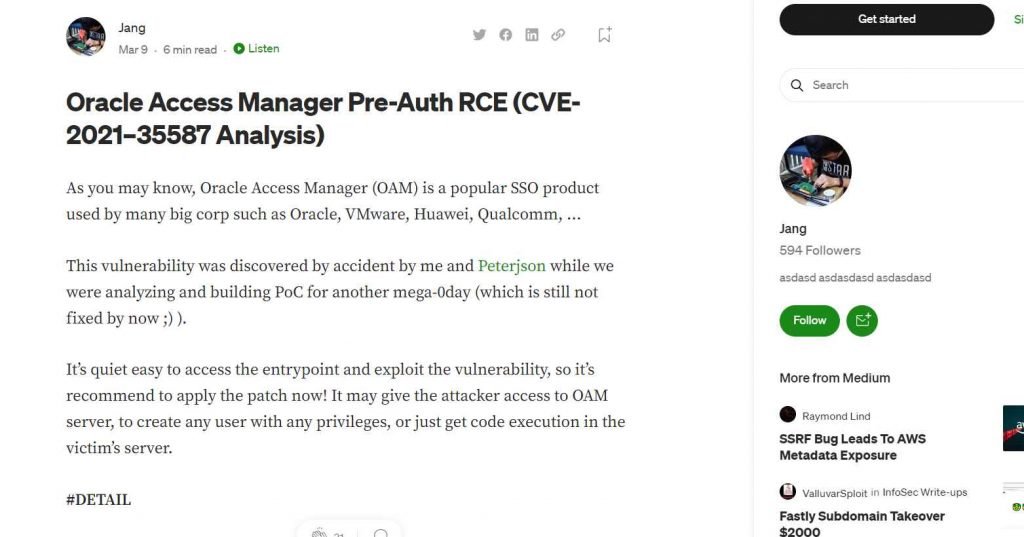
When security researchers “Jang” (Nguyen Jang) and “Peterjson” were “developing PoC for another mega-0day” in the latter half of 2021, they made an unintentional discovery that led to the discovery of CVE-2021-35587.
Oracle Access Manager is a software that is extensively used by businesses for single sign-on (SSO) as part of the Oracle Fusion Middleware suite. The vulnerability exists in the OpenSSO Agent component of the Oracle Access Manager product.
Jang explained earlier this year that it may enable an unauthenticated hacker with network access via HTTP to compromise Oracle Access Manager and use it to either create users with any privileges or execute malicious code on the victim’s server. This was one of the vulnerabilities that was discovered earlier this year.
The security threat affected versions 11.1.2.3.0, 12.2.1.3.0, and 12.2.1.4.0 of Oracle Access Manager and has been patched in those supported versions. However, according to Jang, it also affects Oracle Weblogic Server 11g (10.3.6.0) and OAM 11g (11.1.2.0.0), both of which were discontinued as supported products on January 1, 2022 and do not have a patch available for this RCE vulnerability.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.











