A critical flaw in the Linux kernel has been identified by a security expert (CVE-2022-2964, CVSS score: 7.8) that an adversary may use to execute arbitrary code.
An adversary might utilize the CVE-2022-2964 flaw to run arbitrary code or bring about a DoS attack on the system by delivering a specifically designed request.
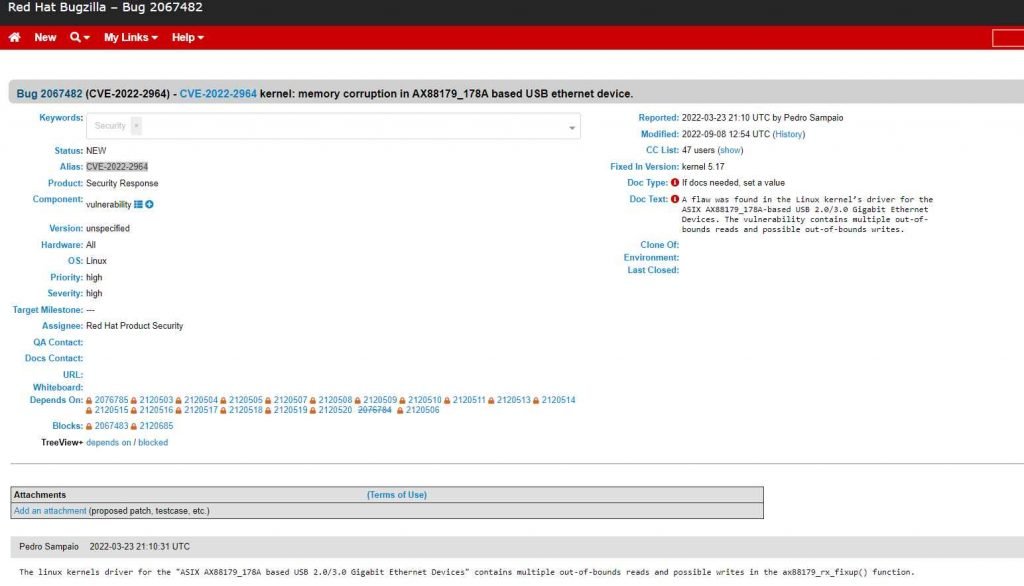
Currently, security fixes have been formally released by Linux kernel maintainers. It is advised that users update Linux servers right away and install other distro’s fixes as soon as they become available. Make sure your Linux distribution is running Linux kernel 5.16.10 or a later version.
Reason Behind the flaw
Multiple out-of-bounds reads and potentially out-of-bounds write flaws in the driver for ASIX AX88179 178A-based USB 2.0/3.0 Gigabit Ethernet Devices were the root of the problem. The ax88179 rx fixup() method in the Linux kernel’s driver for “ASIX AX88179 178A based USB 2.0/3.0 Gigabit Ethernet Devices” has several out-of-bounds reads and potential writes.
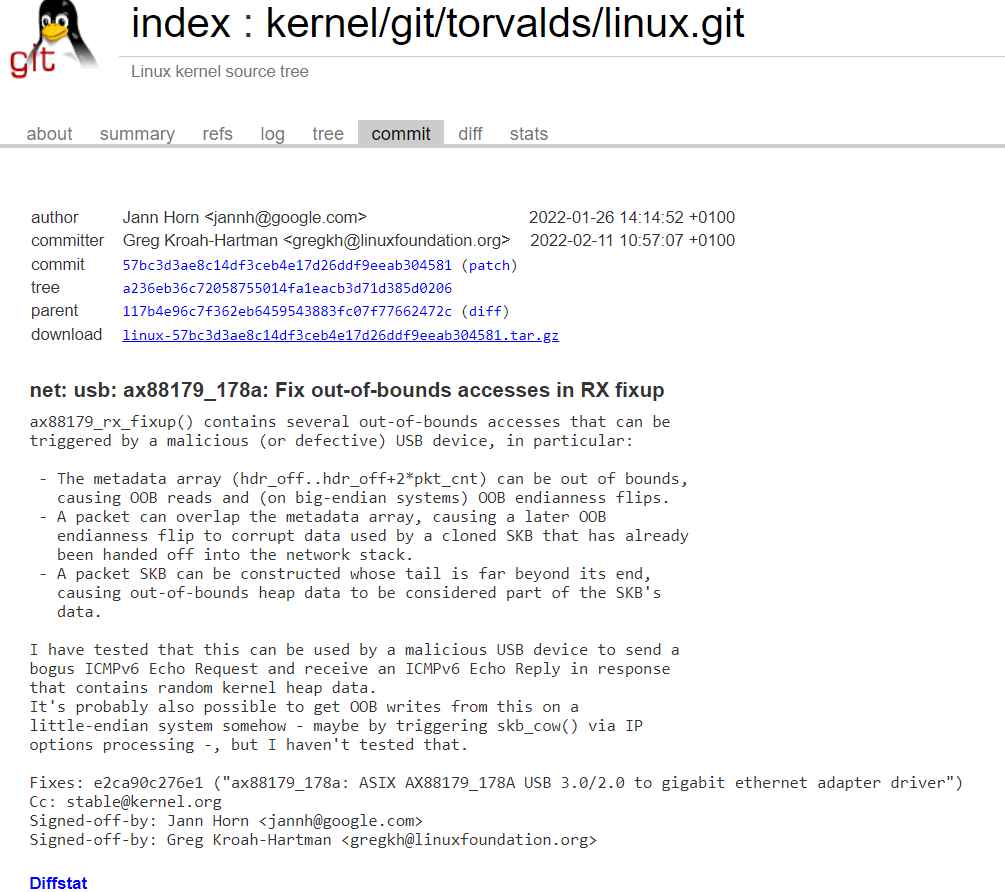
Several out-of-bounds accesses in x88179 rx fixup() can be caused by a malicious USB device, specifically:
Out of bounds reads and OOB endianness flips can result from the metadata array being too large.
An overlapping packet can damage data utilized by a cloned SKB that has already been sent into the network stack due to a subsequent OOB endianness flip.
Out-of-bounds heap data can be included in a packet SKB by creating one with a tail that extends long past its end.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.











