Facial Liveness Verification (FLV) technology is one of the most modern security implementations, currently used for identity authentication in web domains that require the highest user verifications. Despite the fact that multiple cloud service providers already offer this solution and it is in a process of widespread adoption, it is still unknown how far the security risks in this technology can go.
Research by experts from Pennsylvania State University, Zhejiang University and Shandong University investigates the intrinsic characteristics of FLV, its operation in real scenarios and, most importantly, the security risks to which this technology could be exposed and to what extent.
The work of these specialists led to the development of LiveBugger, an attack framework powered by deepfake technology that would allow threat actors to evade FLV protections in real time and in an automated way. This framework allowed the researchers to empirically analyze a set of FLV platforms, making some interesting findings.
Below we will delve into the use of FLV and why it is important that this technology is adequately protected against the malicious use of deepfake and other similar techniques.
The new form of authentication
This technology was implemented as an alternative to legacy passwords and consists of validating the identity of an online user from an image or video of their face. More and more online platforms are using FLV thanks to its low hardware requirements and apparent reliability. Banks, social media platforms, or government services using FLV require the user to capture their face in an image or video that will need to be sent to an FLV API for verification, thus preventing potential threat actors from entering these platforms with stolen usernames and passwords.
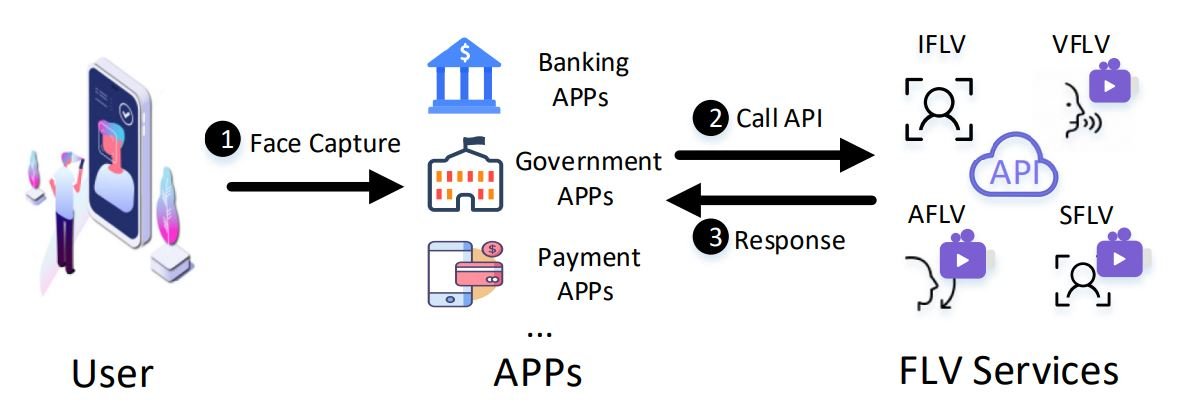
In addition to the fact that its implementation is not a highly complex and demanding process, its mass adoption will be easier thanks to the fact that cloud platforms have begun to provide FLV technology as a Platform as a Service (PaaS), reducing costs and accelerating their operation. That is why specialists estimate that this market will reach a value of more than $ 16 billion USD by the end of 2024.
The accelerated growth in the implementation of FLV for a moment left aside the security analyses related to this technology, something not recommended considering that the potential security flaws in FLV could be inherited by later versions, which would affect millions of users, especially those who must authenticate in FLV PaaS services.
Early analyses on FLV technology focused on the potential use of images of the affected user to arbitrarily enter facial recognition systems, so these were the first security risks addressed by developers of FLV solutions. Although it was necessary to implement these security measures, specialists considered that this did not answer a fundamental question: How efficient are FLV systems against deepfake?
Specialists believe that the use of deepfake technology would allow more sophisticated attacks against FLV implementations, since that technique is capable of generating a realistic movement in an image created from public access sources, whether social network profiles, email accounts, etc., something that conventional FLV attacks could not materialize.
In addition to the mere existence of deepfake technology, the little experience that its use demands is another key risk factor to consider, since the less complex a cyberattack is, the more risk there will be to find this attack replicated in real scenarios.
Assessing FLV Authentication Security
LiveBugger, the framework developed by this research team, integrates various techniques of the most advanced deepfake for the evaluation of an FLV security risk that until then had not been explored in real scenarios.
Broadly speaking, LiveBugger depends on three key elements:
- Intelligence Engine: Provides a full set of authentication features supported by leading FLV PaaS providers. This engine automatically validates FLV defense features using a fully probe dataset
- Deepfake Engine: The first version of the framework integrates six advanced deepfake techniques with which LiveBugger will be able to synthesize all the fake videos necessary to successfully evade FLV authentication
- Analytics Engine: Includes a set of customizable metrics with wealth of information available to support detailed FLV assessment
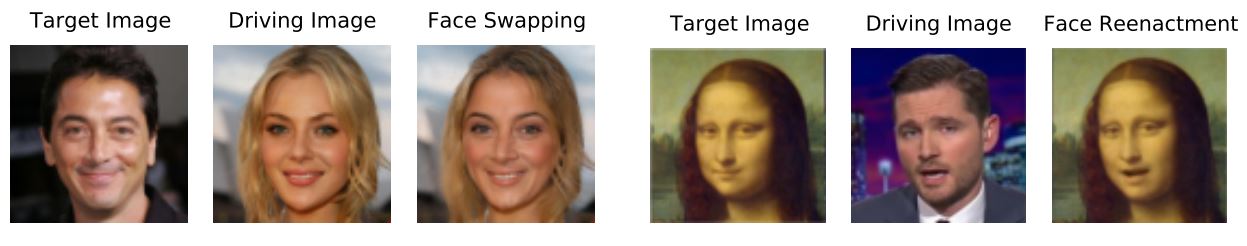
Test results
LiveBugger evaluates the most representative FLV APIs in detail, including those based on image, voice, and motion. Thanks to this analysis, the researchers discovered very interesting features, including:
- Most FLV PaaS implementations do not have deepfake detection mechanisms in their APIs
- Those providers using anti-deepfake mechanisms showed worryingly low results during the analysis
- The performance of FLV systems with random processes (using random voice codes or action sequences) is barely acceptable relative to default FLV authentication
Although FLV solutions continue to advance as expected, so will deepfake technology, so the researchers believe that this is a good time for providers of these services to implement all the necessary security measures to prevent abuse of this authentication mechanism.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.










