Despite the existence of tools for the protection of digital content, piracy always seems to be one step ahead of security teams on streaming platforms, which are simply not able to stop the leakage of their content outside their own platforms.
Platforms such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+ and others use tools such as Widevine DRM, a technology developed by Google for the protection of digital content. Widevine DRM includes three levels of security, with L1 being the most secure of all. Despite their advanced development and recognized capabilities, these kinds of tools can be compromised using various methods.
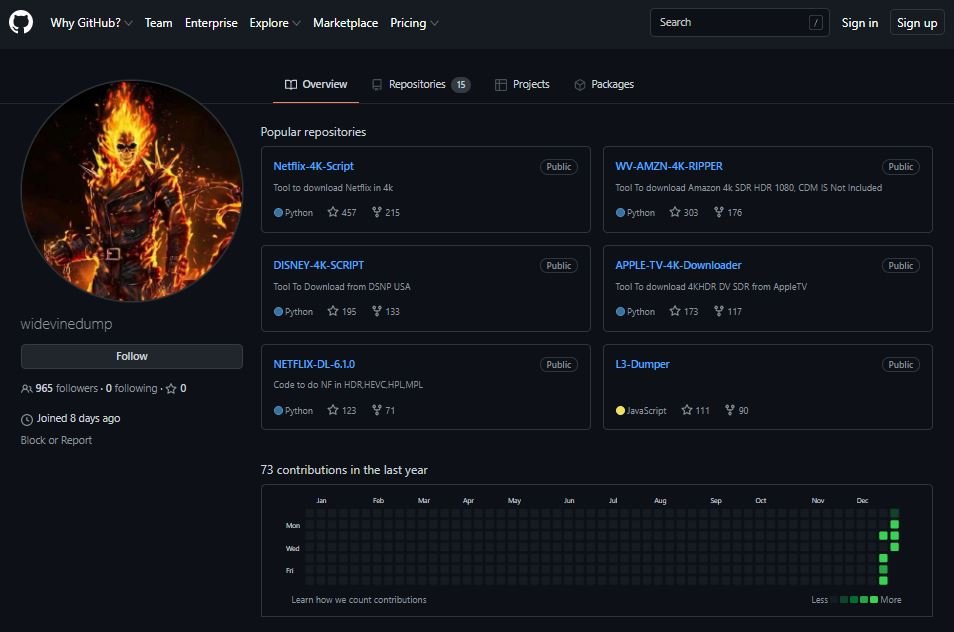
One such method for downloading content was recently revealed on GitHub, where a user identified as “Widevinedump” posted various repositories with tools that allow any user to download HD videos from major streaming platforms.
While the code is completely free and seemingly easy to use, it is necessary to mention that it might not be really safe, so its use is left to each person’s consideration.
The user posted a set of tools identified as DISNEY-4K-SCRIPT, Netflix-4K-Script, WV-AMZN-4K-RIPPER, HBO-MAX-BLIM-TV-Paramount-4k-Downloader, APPLE-TV-4K-Downloader and several other tools, ensuring that they all work and are maintained regularly.
It all sounds too good and really easy, although there is always something behind these tools. Although this time it is not a virus, the trick is that widevinedump tools do not include the content decryption module, necessary to download content in 4K quality.
To access this module, users must pay a developer, which is possible by contacting Widevinedump, who even left their own email address for contact. Even though this toolkit is incomplete and may be insecure, it will surely prove useful to some users and developers.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.










