Remote access Trojans (RATs) are one of the most popular hacking tools, as they allow attackers to remotely control a compromised system. These powerful malware variants are always being updated in order to evade security measures on attacked systems, so it is necessary to know as much information as possible about it.
This time, the experts from the malware analysis course of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) will show you the 6 variants of remote access Trojan most used by the cybercriminal community. Remember that this article was prepared for informational purposes only and should not be taken as a call to action; IICS is not responsible for the misuse that may occur to the information contained herein.
Below is a list of the malicious tools that will be analyzed:
- Cerberus 1.03.5
- CyberGate 1.07.5
- DarkComet 5.3
- Orcus RAT 1.9.1
- NjRat Danger Edition 0.7D
- Venom 2.1
It is worth mentioning that the experts of the malware analysis course have evaluated these Trojans according to the criteria mentioned below:
- Features
- Speed of implementation in the target system
- Load capacity
- Build code protection level
- VirusTotal Check
- Pros and cons in general
Considering the above, let’s continue to the analysis of RATs.
Cerberus
This tool is capable of working at a high speed, as its load only takes 5 seconds. During operation, the RAT takes up about 7.3 MB of memory, so it does not represent a load on the target system. In addition, according to the experts of the malware analysis course, this RAT is able to evade security mechanisms with the appropriate encryption.
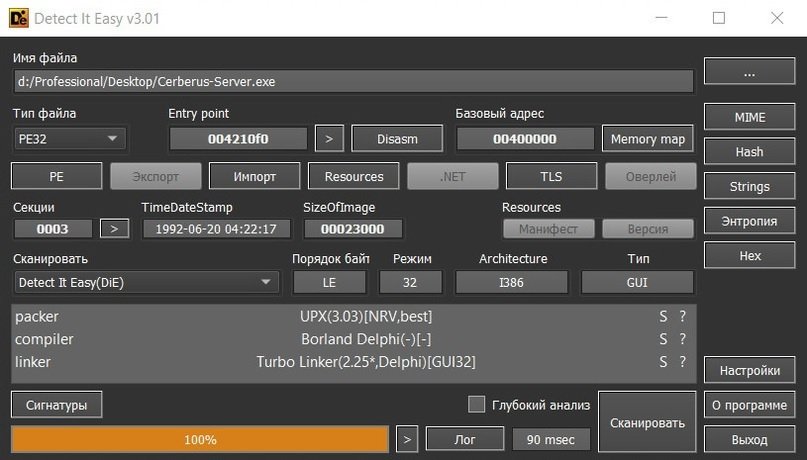
Cerberus has the ability to change language, recognize various output formats and even add sounds that will be activated at startup. This RAT can also generate persistence in the system and is very functional to deceive the target user, although it can be easily detectable. Another disadvantage is that the compiler is somewhat outdated, which can be problematic for the attacker.
CyberGate
According to the experts of the malware analysis course, booting this RAT takes around 25 seconds, so it is significantly slower compared to options like Cerberus. Booting CyberGate is also somewhat eye-catching, as it creates several processes visible in the task manager.
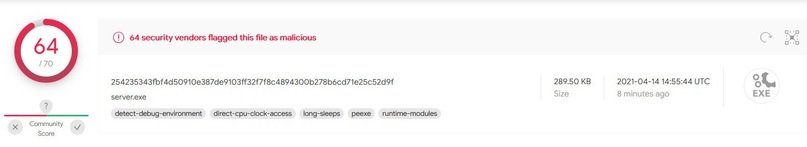
As for the scan on VirusTotal, only one of the 70 most popular antiviruses was able to determine the actual origin of this RAT.
While it is easy to use CyberGate to collect a lot of information from active sessions, the experts of the malware analysis course believe that it would be easy for any administrator to detect and remove the infection.
DarkComet
The compilation of this malware takes about a minute, which makes it a very slow option for this class of tools, although once compiled it considerably reduces its activity, consuming only 2.7 MB of the system.
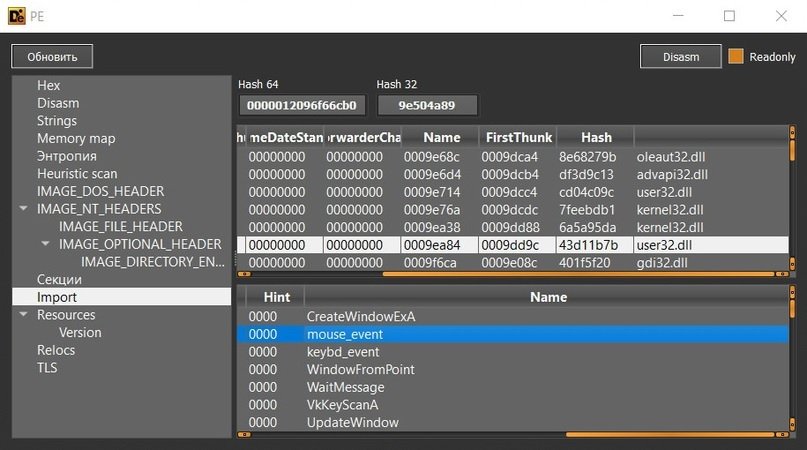
The construction is not hidden with protectors or packers of any kind and, during import, you can immediately notice user32.dll, from which the mouse and keybd modules are imported, and, of course, the VkKeyScanA keylogging function.
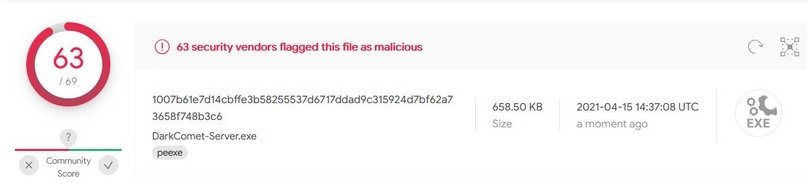
Among its outstanding functions is the use of two modes of virus creation, the programming of actions and the creation of RAT download links, note the experts of the malware analysis course.
While its resource consumption is discreet and there is not much information about DarkComet in VirusTotal, this RAT is not able to hide its activity properly, so it is not a very popular option.
Orcus RAT
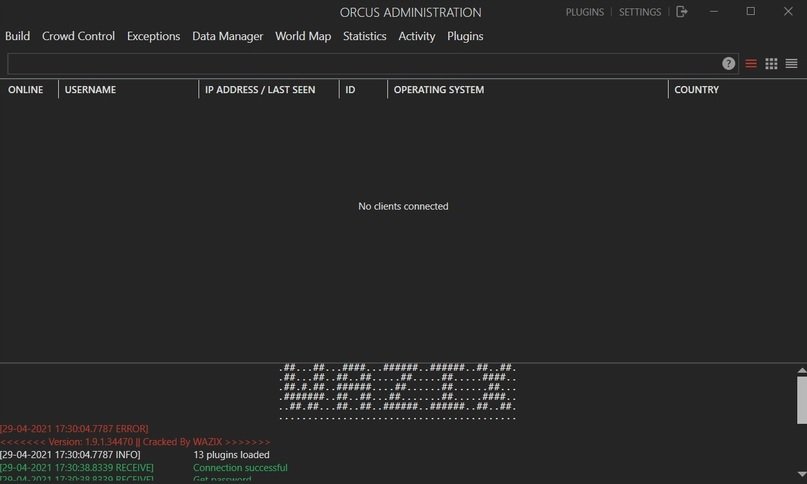
This RAT variant assembles in less than 10 seconds, consumes approximately 15 MB in RAM and does not create strange processes on the target system, in addition to having encryption, note the experts of the malware analysis course. Intentionally, Orcust RAT may create third-party processes for distraction purposes and accepts some plugins to enhance its capabilities.
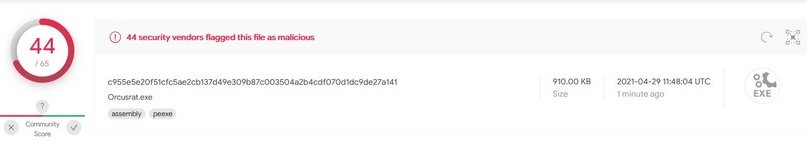
Many antivirus can detect Orcus RAT, although this does not mean that they are safe from this malicious development; however, the functionality of the RAT is limited if the attacker does not have some plugins.
NjRat
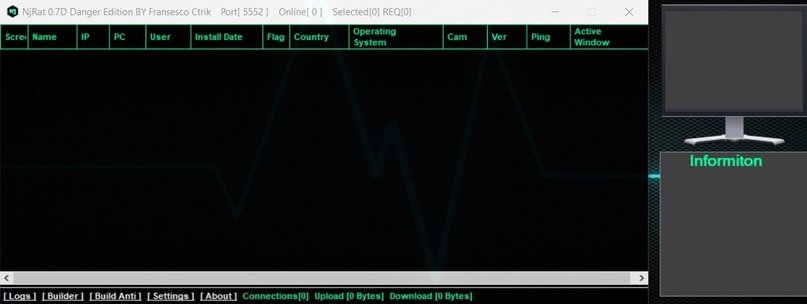
According to the experts of the malware analysis course, this RAT has advanced features, including the ability to stop when detecting specific processes, share the victim’s screen, disable the task manager and the impossibility of uninstalling it.
On the other hand, its assembly takes exactly ten seconds and takes up 18% of the capacity of the processor, so it can be striking. The antivirus scan throws better results than the options shown above, although this does not mean that it is impossible to detect.
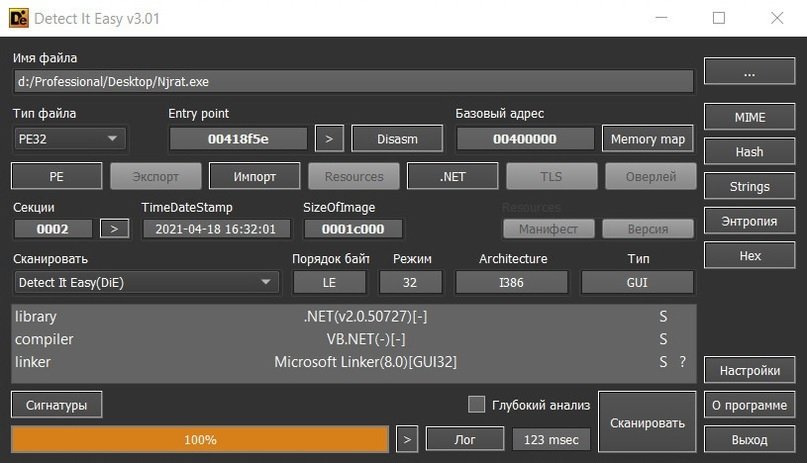
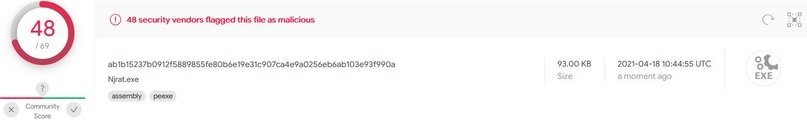
While researchers believe that there are better options in the cybercriminal community, NjRat account is a fully functional hacking tool, but its main disadvantage is the high consumption of processor resources.
Venom
According to the experts of the malware analysis course, this RAT can load a build into AnonFile, in addition to being able to add very well hidden installers, even with false installation licenses. Attackers using Venom will also be able to create a rootkit and modify the Trojan, providing a high level of customization.
Launching this RAT takes about 20 seconds and the build takes 9 MB of RAM, so it consumes virtually no system resources. It is written in .NET and although it requires better concealment tactics it is not possible to see the code on the fly.
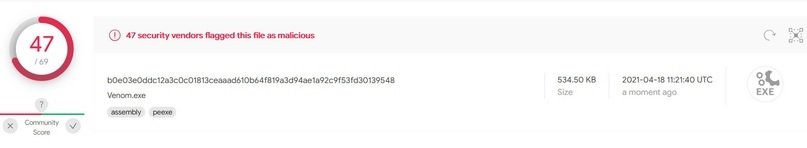
Venom is perhaps the best option on this list, as it easily adapts to the characteristics of each attack campaign and virtually no antivirus can detect the infection. The main downside of Venom is that it’s a paid RAT, though that’s certainly not something that stops an advanced hacking group.
Conclusion
This is just a sample of all the malicious tools considered as RATs, as it would be practically talking about all the functional options in just one article. As if that were not enough, the experts of the malware analysis course point out that there are groups that use clients like TeamViewer for malicious purposes trying to emulate the characteristics of a Trojan, so hackers have a lot of resources.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.











