Man-in-The-Middle (MiTM) attacks are one of the most popular hacking techniques nowadays, and occur when a third party arbitrarily breaks into an established network session or in a data transfer process. As the name suggests, the attacker is placed in the middle of the data transmission path in order to usurp the place of a legitimate actor.
According to cybersecurity specialists, this practice can be highly harmful to any organization, especially those that control confidential information. Typical consequences of a MiTM attack include theft of login credentials, interception of financial information, and bank fraud.
Among the most common MiTM variants are:
- Packet detection: Threat actors use a variety of tools to inspect network packets at a low level, allowing threat actors to view data packets that they would not have access to under normal circumstances
- Packet injection: A threat actor could inject malicious packets into data transmission channels, a stage that comes after analyzing the target network in order to determine how and when to send malicious packets
- Session hijacking: Most web applications generate a temporary session token when logging in for easy later access. Threat actors can employ tracking tools to identify and use session tokens as if they were a legitimate user
- SSL removal: Threat actors can employ an advanced technique for disabling SSL and intercepting legitimate packets in order to modify HTTPS-based requests and redirect them to a destination controlled by hackers
Given the dangerousness of this hacking variant, it is important that IT administrators have the most updated information and tools to identify, contain and counter this threat. This time, cybersecurity specialists from the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) will show you the best tools to search for and address flaws related to MiTM attacks.
As usual, we remind you that this article was prepared for informational purposes only, so IICS is not responsible for the misuse that may be given to the information contained herein.
Hetty
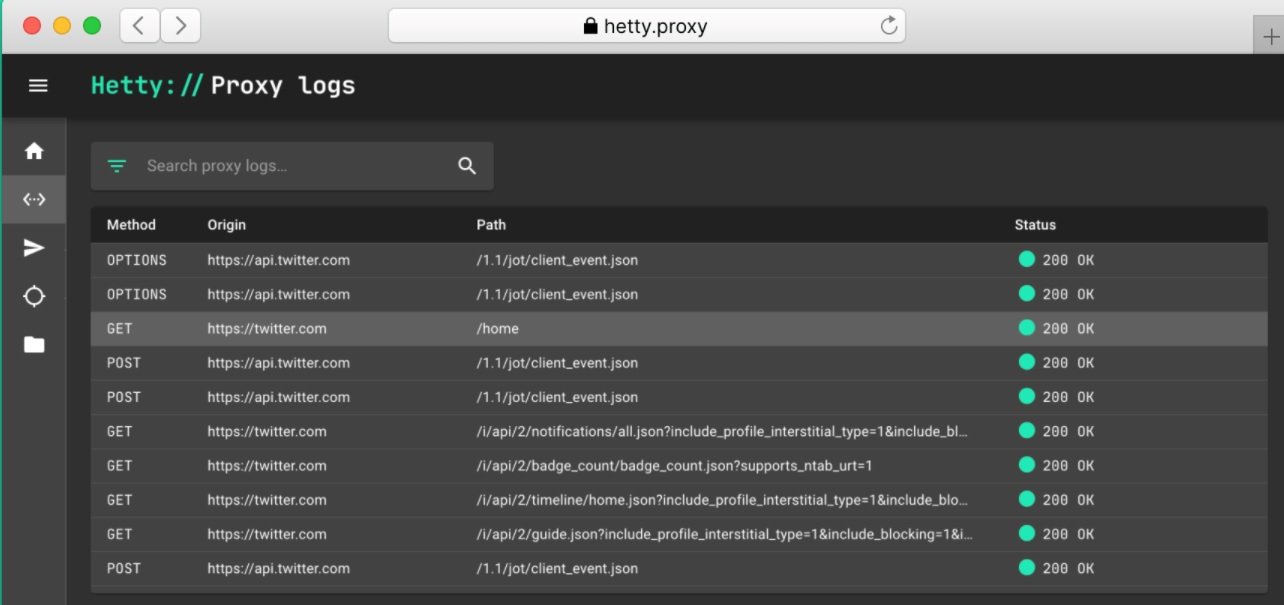
Hetty is an open source HTTP toolkit with really useful features for any IT administrator or researcher. This is a very lightweight tool that includes a built-in Next.js interface, plus a MiTM proxy.
Cybersecurity experts consider Hetty an attractive tool because it allows full-text search and has a module for sending manual HTTP requests. In addition, the tool has an attacker module for automatically sending HTTP requests and is very easy to install and use.
Bettercap
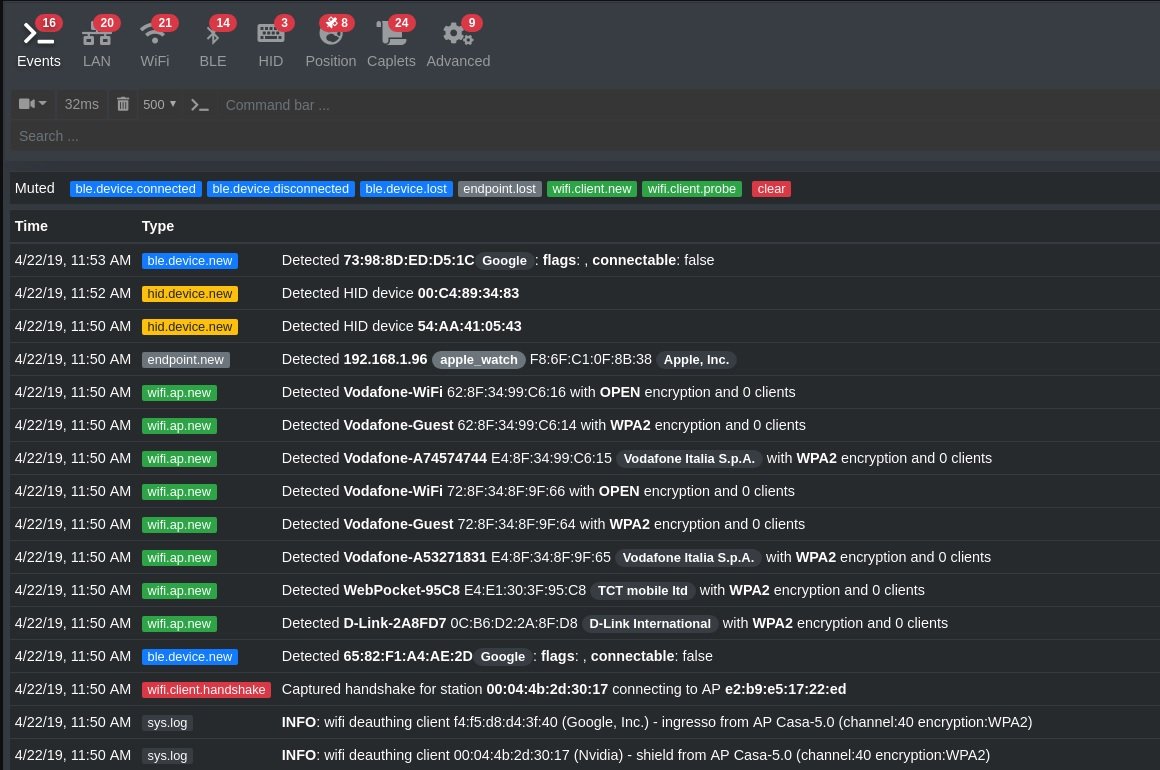
This is a complete network attack and scanning tool that provides researchers and cybersecurity experts with all the capabilities required for scanning or attacking WiFi, IPv4, IPv6, Bluetooth connections, and wireless device connections through other protocols.
Bettercap also has modules for network monitoring and other functions, including the creation of fake access points, password identification and DNS spoofing.
Among its main advantages are its powerful access credential tracker and a powerful MiTM vulnerability scanner. Bettercap also stands out for its user-friendly interface and the ability to monitor and manipulate TCP, HTTP, and HTTPS traffic in real time.
PROXY.PY

This is an open source proxy server for WebSockets, HTTP, HTTPS, and HTTP2. According to cybersecurity experts, users can find this tool in a single Python file, allowing them to inspect target web traffic, including encrypted TLS applications.
This is a tool noted for its ability to manage thousands of connections per second, as well as controlling programmable functions such as built-in web servers, proxies, and HTTP routing customization. The tool does not consume large system resources (between 5 and 20 MB of RAM), in addition to being based on the standard Python libraries and does not require the installation of external dependencies.
Finally, PROXY.PI has a fully customizable control panel in real time and that can be extended by adding plugins, in addition to using rTLS to provide end-to-end encryption between the tool and the client.
MITMPROXY
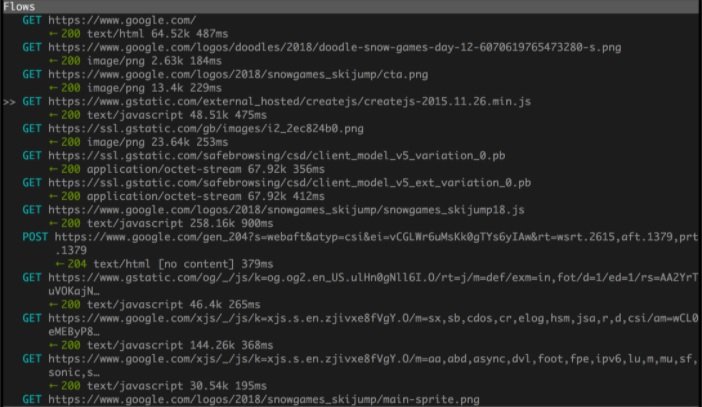
This is an easy-to-install and easy-to-use open source HTTPS proxy solution, cybersecurity experts say. The tool has a console interface that allows researchers to verify and manipulate traffic flow in real time.
MITMPROXY is actually composed of three different tools: MITMPROXY (console interface), MITMWEB (web interface) and MITMDUMP (command line). Cybersecurity researchers can use the command-line tool as an HTTP or HTTPS proxy to log all traffic from the target network and view user requests.
In general, this is an interactive and highly reliable tool for the analysis and manipulation of HTTP traffic, characterized by its flexibility, stability and ease of use, as well as allowing the recording and saving HTTP conversations on the client and server side to later reproduce and analyze them.
BurpSuite
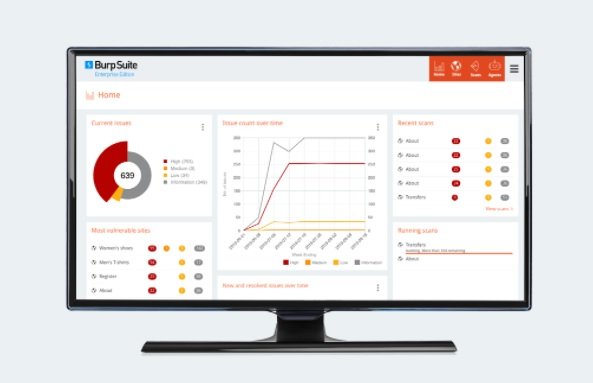
This is a tool for automated vulnerability scanning of great use for the ethical hacking and cybersecurity community. Researchers can use this tool to test vulnerabilities in web applications to prevent the deployment of MiTM attacks.
Using it as a web proxy, BurpSuite becomes an intermediary between the web browser and the target server; hence it allows intercepting, analyzing and modifying the traffic of requests and responses.
For cybersecurity experts, the most attractive capabilities of this tool are the ability to intercept and analyze raw web traffic between the web browser and the server. BurpSuite can also break the TLS connection in HTTPS traffic between the browser and the target server, allowing it to act as an attacker and modify the compromised data. The automatic vulnerability scanner is also one of the main advantages when using this tool.
Ettercap

This is an open source tool for analyzing and intercepting network traffic. Ettercap allows cybersecurity experts to analyze all kinds of hosts and network protocols. Users can also log packets on the local network and other environments, as well as analyze network traffic for MiTM attacks.
Ettercap allows users to intercept network traffic and sensitive information such as passwords, in addition to decrypting encrypted data and extracting user credentials on the analyzed networks. Ettercap also supports deep information analysis and network protocol analysis, including encrypted protocols.
On the other hand, the tool allows the analysis of the network topology and the installation of the installed operating systems through a convenient graphical user interface with interactive and non-interactive GUI options.
Conclusions
MiTM attacks are a difficult to detect hacking variant, as they do not occur directly on the target system and hackers do not perform suspicious-looking actions once installed in the middle of the affected connection. However, it is possible to use some techniques to prevent the most common MiTM variants.
Among the main recommendations to mitigate the risk of MiTM attack, cybersecurity experts list:
- Protect Internet connections on home or business networks, using effective solutions for the security of connected devices
- Implement strong WEP/WAP encryption for access point protection
- Verify that all sites visited are secure and have HTTPS in their URL
- Avoid suspicious-looking websites and emails
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.











