Pentesting has become one of the main practices of the cybersecurity community and even represents an important source of income for independent researchers and security firms. The most advanced security audits are typically performed on Kali Linux computers with specific hardware requirements, although some scanning processes can be performed using a conventional smartphone or tablet.
In this article, pentesting specialists from the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) will show you the best 14 apps to perform basic security scans from a mobile device running Android operating system. It is important to note that it is possible to perform some hacking tasks from our smartphone; we only have to learn to distinguish between the really useful tools and the junk apps that abound on platforms like Google Play Store.
HACKING VIA SMARTPHONE TOOLS
Pentesting experts classify hacking apps for Android into the following categories:
- Web resource scanners: These are hacking tools to find vulnerabilities in web applications
- Combinations: Allow users to search for hardware and software vulnerabilities to exploit them. These tools let deploying tracking attacks, Man-in-The-Middle (MiTM) attacks, among other hacking variants
- Trackers: These are hacking apps to intercept and analyze target user’s traffic
- Help utilities: Support tools during pentesting
- Directories and search engines: Applications that perform auxiliary functions
Let’s look at some good examples of these tools.
WEB RESOURCE SCANNERS FOR ANDROID
Web application scanners are probably the most important mobile hacking resource, as mentioned by pentesting experts. Here are three applications that will allow you to find open management dashboards, reset passwords, as well as testing any website for XSS vulnerabilities, SQL injection capabilities, directory list compilation, and more.
Kayra the Pentester Lite

Kayra the Pentester Lite is a vulnerability scanner to analyze the configurations of a specific web server that attempts to obtain a list of directories and includes additional tools, such as hashing generators and AES decryptors, as mentioned by pentesting experts.
The application has simple and direct configurations. It supports HTTPS and validates TLS, plus it is capable of searching for XSS, brute force flaws and performing dictionary attacks. It can work in the background and in multithreaded mode. It contains the Google Hacks database and automatically detects known vulnerabilities. The free version is quite functional, but if you want to get rid of the ads the paid version is accessible. The latest version of Kayra the Pentester Lite (v1.4.0) requires only 4.7 MB and works on any Android 4 device without rooting.
DroidSQLi

DroidSQLi allows you to verify websites for SQL injection vulnerabilities in different variants:
- Normal SQL Injection: The classic version with the union ALL SELECT parameter step
- Error-based SQL injection: Conscious use of incorrect query syntax to receive an error message that reveals additional database parameters
- Blind SQL Injection: A series of queries that analyze true or false DBMS responses, allowing you to restore the database structure
- Time-based SQL injection: the formation of additional queries that cause the DBMS to be suspended for a certain period of time, making it possible to retrieve the data character by character
This utility automatically selects the injection method and also uses techniques to bypass query filtering. To start testing the site, you must manually search for the entry point. Typically, this is the address of a web page that contains a query such as Id x or P x, where X is a positive integer. In our example, the payload of the ID parameter looks like this:
id=(SELECT 4777 FROM(SELECT COUNT(*),CONCAT(0x71626b6a71,(SELECT (ELT(4777=4777,1))),0x7170767871,FLOOR(RAND(0)*2))x FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PLUGINS GROUP BY x)a)
There are many websites that are vulnerable to SQL injection and it is best to find these flaws through a browser search.
This utility does not require a rooted smartphone and works on all Android versions later than 5.2.
Droidbug Admin Panel Finder FREE
This application searches management panels by default addresses of different CMSs. The result of this work does not always correspond to the actual state of things, as IDS and WAF are installed on popular web servers and have better security mechanisms.
Despite this, on less popular sites with poorer security measures everything is very grim and you will find a valid admin panel in a matter of seconds. The paid version removes ads and unlocks the ability to use brute force attacks in a mixed pattern for sites with PHP/ASP/CGI/CFM/JS support.
The latest version of Droidbug Admin Panel Finder FREE needs only 6.4 MB and does not require rooted devices.
COMBINATIONS TO HACK FROM A SMARTPHONE
The Internet isn’t just about web applications. The following collection of hacking apps for Android will allow you to search for vulnerabilities in software and hardware, perform sniffing, MiTM attacks, and backdoors, among other variants.
cSploit
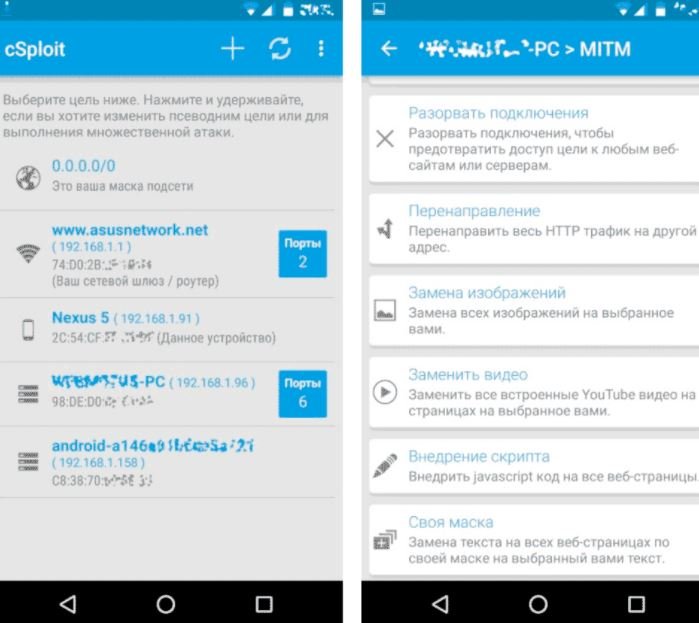
This is one of the most powerful tools for scanning networks and finding vulnerabilities on detected hosts. Experts can use cSploit to draw a network map and find information about all connected devices.
The tool also allows you to determine the IP/MAC and provider, determine the operating system, look for vulnerabilities using the Metasploit RPCd framework and obtain passwords using brute force.
The latest version (v1.6.6 RC2) requires 3.5 MB and works on all Android versions later than 2.3, although it should be noted that cSploit requires a rooted device to properly work.
dSploit
If cSpoit worked for me smoothly, the last three versions of dSploit failed with an error almost immediately after release. Since developer Simone Margaritelli got a job at Zimperium, dSploit’s developments have become part of zAnti’s proprietary utility.
This utility requires a rooted Android device to work properly.
zANTI

This is a mobile pentesting app developed by Zimperium whose interface is divided into two parts: Scanning and Man-in-The-Middle (MiTM). A separate function allows users to identify vulnerabilities in the pentesters’ own smartphone.
This tool helps researchers to hack routers and get full access to them. Using MiTM attacks, zAnti detects unsecured items at three levels: in the operating system, applications, and device settings.
Finally, the tool prepares a report that contains explanations and tips on how to eliminate the detected flaws. Like other tools in this list, zANTI requires a rooted device.
SNIFFERS TO INTERCEPT TRAFFIC ON ANDROID
No pentester can do without good sniffer software, pentesting experts mention. Therefore, the next section of the article is dedicated to applications for intercepting and analyzing target user traffic.
Intercepter-NG
This is an advanced tracker for MiTM attacks. Intercepter-NG captures traffic and analyzes it on the fly, automatically detecting the authorization data contained.
The tool automatically detected data formats include passwords and hashes for the following protocols: AIM, BNC, CVS, DC++, FTP, HTTP, ICQ, IMAP, IRC, KRB5, LDAP, MRA, MYSQL, NTLM, ORACLE, POP3, RADIUS, SMTP, CALCETINES, Telnet, and VNC.
This app works on any Android device after v2.3, although it is important to mention that a rooted device is required, as mentioned by pentesting experts.
Packet Capture
This is a simple and legal TCP/UDP packet analyzer with the ability to intercept HTTPS sessions using MiTM. Using this tool does not require root rights as it uses Android’s built-in feature to send traffic over a VPN and forge an SSL certificate.
Packet capture works locally and does not perform ARP impersonation, session hijacking, or other attacks on external hosts. The application is positioned as a proxy to debug and downloaded from official websites.
HELP UTILITIES
While advanced pentesting utilities require rooted devices and other tools, there are simpler apps available in the Play Store and work on any smartphone, pentesting experts mentioned.
WPSapp

This program scans for WPS-enabled access points. After finding them, it tries testing the default pins on them. They are few and are known from router manufacturers’ manuals.
If the user did not change the default pin and did not turn off WPS, then the utility will review all known values and get WPA(2)-PSK, no matter how long and complex. The wireless password is displayed on the screen and is automatically saved in the WiFi settings of the attacking smartphone.
This tool works on all versions of Android after 5.1 and, although it does not necessarily require a rooted device, its operation could improve in case of using a jailbreak.
WiFiAnalyzer

This is a free and open source WiFi scanner very useful for detecting access points, knowing their parameters, measuring the signal strength and the distance between the different WiFi points.
WiFiAnalyzer allows you to view connection status, filter targets by signal strength, SSID, frequency used (2.4/5 GHz) and encryption type. You can also manually determine the least saturated channel using the available graphs, mentioned by pentesting specialists. Using this tool does not require a rooted device and works on any version of Android higher than v4.1.
Fing
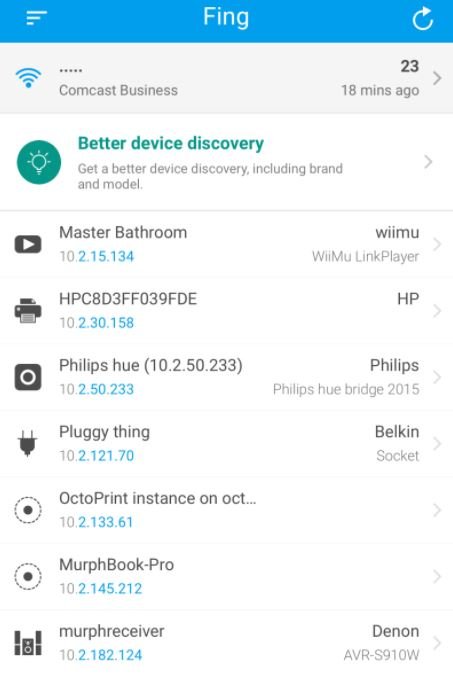
Fing is a tool available on the Google Play Store to perform quick scans of the WiFi network to which our device is connected, identifying all users connected to this access point. Although the main use of this tool is to analyze our own WiFi network, Fing has other very attractive options.
Its Premium version can perform advanced analysis of the NetBIOS, UPNP, and Bonjour names, so you can fully identify the types of devices connected to a network, as well as having built-in ping and traceout utilities and sending Wake on LAN (WOL) requests, cybersecurity experts mention.
As it is an application available on official platforms, users do not require a rooted device to access all Fing features.
NetCut
This app detects all devices connected to a wireless network, as well as using advanced mechanisms to eject intruder devices or even restrict full access to the administrator’s WiFi network.
The app requires only 12 MB and works on any version above than 4.0, although a rooted device is required.
DIRECTORIES AND SEARCH ENGINES FOR PENTESTING
Finally, we’ll address a couple of utilities that, while not directly related to hacking activities, perform helper functions to develop this kind of testing.
Droidbug Exploiting FREE

This utility was designed to find and download various types of exploits, grouped into two categories: local execution and remote execution. A separate group includes hardware and web vulnerabilities, as well as those used in denial of service (DoS) attacks.
This tool can be run by any version of Android greater than 4.0.3, although its execution requires a rooted device.
Pentest Chearsheet

According to pentesting specialists, this is a complete guide to running security tests according to The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) guidelines.
This guide includes a selection of links to hacking utilities tested and grouped according to the task in question, be it online scanning, vulnerability analysis, reverse tools, fuzzers, trackers, among others. This utility weighs only 2.2 MB and works on all Android versions greater than 4.0, plus no rooted device is required for use.
Remember that this material was developed for entirely academic purposes, so its misuse is not the responsibility of IICS. To learn more about computer security risks, malware, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) website.

Cyber Security Specialist with 18+ years of industry experience . Worked on the projects with AT&T, Citrix, Google, Conexant, IPolicy Networks (Tech Mahindra) and HFCL. Constantly keeping world update on the happening in Cyber Security Area.










