2020 has been a prolific year for cybercrime; ransomware attacks, identity fraud and phishing campaigns are reported daily and in increasingly large amounts, as malware reverse engineering experts claim. One of the fastest growing trends is online account hijacking, which allows threat actors to deploy subsequent attacks.
Most account hijacking campaigns rely on the use of brute force attack, password cracking tools, and “account checking” tactics. These are scripts that are used against login portals to illegitimately access users’ accounts.
Criminals can also take advantage of IP addresses, VPN services, botnets or proxy servers to maintain the anonymity of malicious campaigns, increasing their chances of success. If they manage to access the attacked accounts, hackers could use them for illegitimate purposes and even extract their sensitive data for further attacks, such as bank fraud, identity theft, among others.
Account hijacking campaigns also require an extensive list of credentials, which are obtained from data breaches in private firms or public organizations. The attack then begins, which is usually a process of automated login attempts using multiple malicious tools.
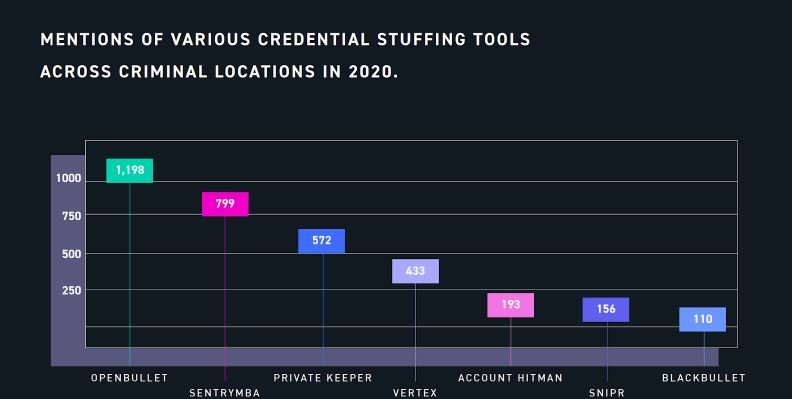
Any hacking group can search for these tools on dark web forums and even on conventional internet. Among the most popular tools for hijacking accounts using lists of credentials are Sentry MBA, Private Keeper, Account Hitman, BlackBullet, Snipr, among others.
Over the past few years the Sentry MBA tool has been a favorite of hacking groups that undertake account hijacking campaigns, although recently a new development has positioned itself as a new favorite of the cybercriminal community. Known as OpenBullet, this tool allows threat actors to make requests to target web applications effectively, facilitating fraudulent activity.
According to a report from Digital Shadows, OpenBullet was launched in March 2019 via GitHub, although it had previously been mentioned on hacking forums hosted on dark web, mentioned by malware reverse engineering experts.
The tool, initially developed for legitimate purposes, includes several useful modules for information collection, automated pentesting, among other tasks. OpenBullet bears a strong resemblance to BlackBullet, another hacking tool, although unlike BlackBullet, it is possible to modify OpenBullet settings at the user’s preference.
Regarding the increase in its use, OpenBullet has made a name in the cybercrime community thanks to its constant maintenance and reduced use of the graphics processing unit (GPU) in the target system, making it a very quiet tool. However, malware reverse engineering experts believe that hackers prefer OpenBullet because of its open source nature, allowing you to customize the methods used by the tool in each attack, based on the skills of threat actors.
In the hacking forums it is even possible to find tutorials on using the tool, adding hundreds of possible settings to the sale. An OpenBullet group of operators even have an online store to offer their services. The official OpenBullet page on GitHub specifies that the tool should not be used for attacks on non-user sites, although there is actually no way to prevent this software from being used for malicious purposes.
As you can see, account hijacking has grown thanks to the wide variety of tools that threat actors can use. Hacking forums act with total impunity, so it is difficult to stop this practice. Law enforcement agencies need to take stronger action against cybercrime, before it is too late.
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.