Ethical hacking specialists from security firm ESET report the emergence of a new banking Trojan tracked in multiple locations in Latin America. Identified as Mispadu, this malicious program uses fake McDonald’s ads and phishing emails to trick victims through websites and social media platforms, primarily Facebook.
In addition to malicious advertising, it is also possible to find this malware on a malicious Google Chrome extension used by campaign operators for the theft of credentials and banking information.
In their report, the specialists say that Mispadu main activity tracking has been recorded in Brazil and Mexico; written in Delphi, this Trojan infects victims in a similar way to other malware variants, deploying pop-ups of malicious content to try to obtain sensitive information, mainly financial details.
In addition, Mispadu has a backdoor feature that allows hackers to take screenshots, simulate clicks and even take keystrokes record. The Trojan also has an update module using an automatically downloadable and executable Visual Basic Script (VBS) file.
Employing Mispadu, threat actors collect multiple details about the victims, including:
- Operating system version
- Device name
- List of security tools installed on the target system
- In the case of Brazil, the Trojan checks if the device has Diebold Warsaw GAS Tech installed, a popular app used to control access to online banking services
As for the distribution of Mispadu, ethical hacking experts mention that there are two main methods: spam and malicious advertising (also known as malvertising). Specialists claim that malvertising is not usually a very common method of distribution of banking Trojans.
Next, we can find two different examples of phishing emails used by Mispadu operators, aimed at people in Brazil and Mexico. (foto)
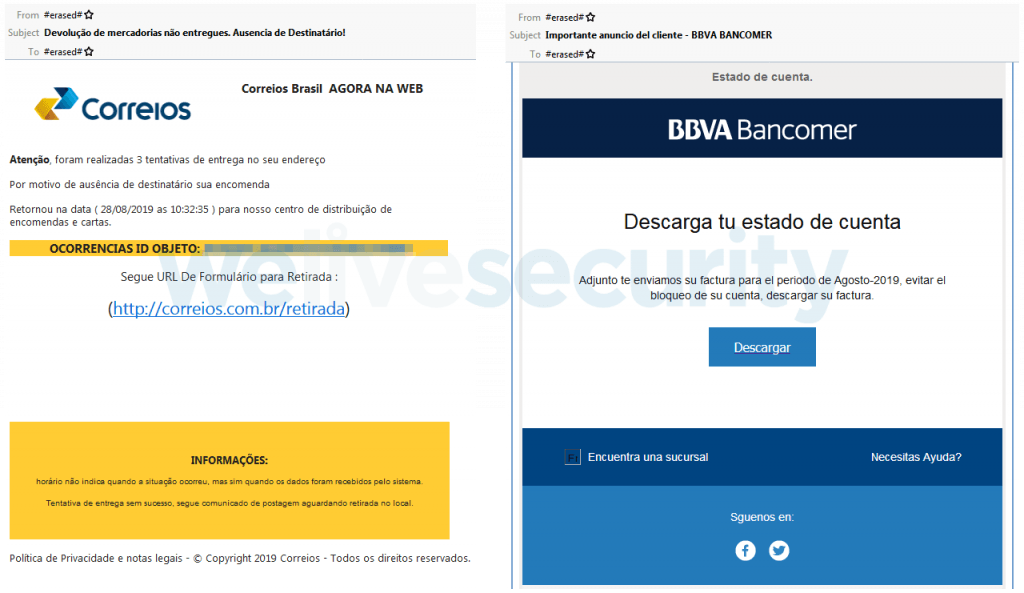
SOURCE: ESET
Another vector of attack is the placement of paid advertising on Facebook; in this case, the attackers decided to use fake discount coupon ads for McDonald’s. When interacting with this fake advertisement, the victim is redirected to a web page from where he is suggested to click on the “Generate Coupon” button, which will start downloading a ZIP file that includes the MSI installer.
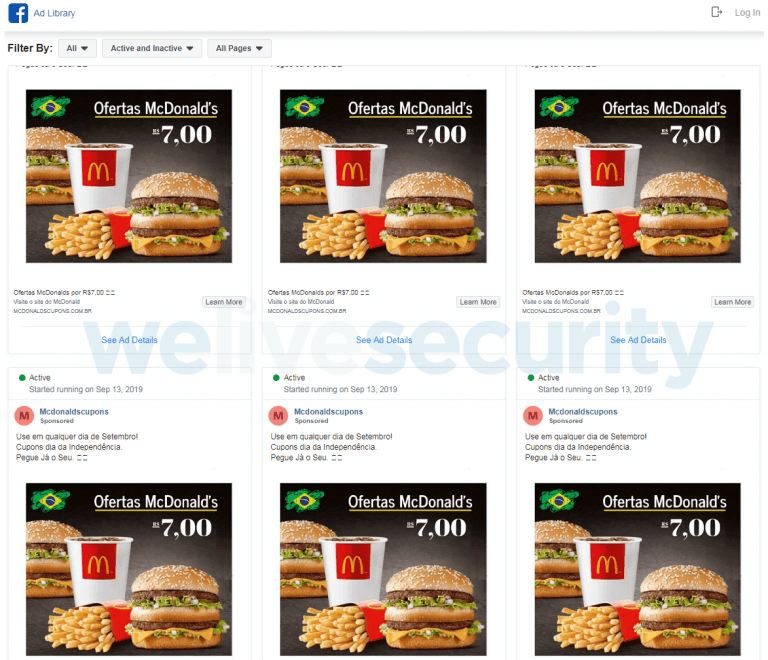

SOURCE: ESET
According to ethical hacking experts, when the victim runs the installer, it initiates a string of three scripts:
- The first script decrypts and runs the following script
- The second script retrieves the third script for execution
- The third script verifies some data from the infected device to identify the country where the victim resides and then configures persistence, creating a link in the home folder and running an injector that will locate the Trojan for decryption and execution
According to the ethical hacking specialists from the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), Mispadu extracts information by scanning the contents of the clipboard of the infected device, it has even been detected that the Trojan is able to identify cryptocurrency wallets used by the victim to then replace them with a hacker-controlled address, although this is not the main means of profit for criminals.
For security users are advised to identify any possible malicious messages received by email, as well as never click on an attached link, as well as ignore any online ads that promise free stuff or that just seems too good to be true.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.










