Although it finished over a year ago, the FIFA World Cup Russia 2018 is still linked to various controversies over information leaks and corruption cases. According to information security specialists, some documents with detailed profiles on several FIFA officials were published through the BlackMirror Telegram channel, specifying how and to whom the Rusian committee should bribe, as well as a method for obtaining votes necessary to win the elections in the soccer organization. The document lists the names of some of the leading members of the organizing committee of the past World Cup in Russia.
In 2010, Russia won the election to host the last FIFA World Cup, beating countries such as England, Portugal and Spain. This decision was the subject of controversy from the beginning, as even Joseph Blatter, former FIFA president, acknowledged that this election, in addition to the election of the 2022 World Cup, to be organized in Qatar, stowed off a corruption scandal that led to in the dismissal of many senior officials of the organization, including Blatter himself.
The leaks consist of a total of 5 folders, including various documents such as:
- A letter from the Deputy Director General of the Russian Organizing Committee 2018 to various Russian officials
- Dossiers on FIFA Executive Committee members. Each dossier mentions personal details (academic background, marital status, etc.), as well as information to try to influence their voting

- A folder with information about other “key actors” for the 2018 World Cup venue election

- A table summarizing the itinerary of Executive Committee members
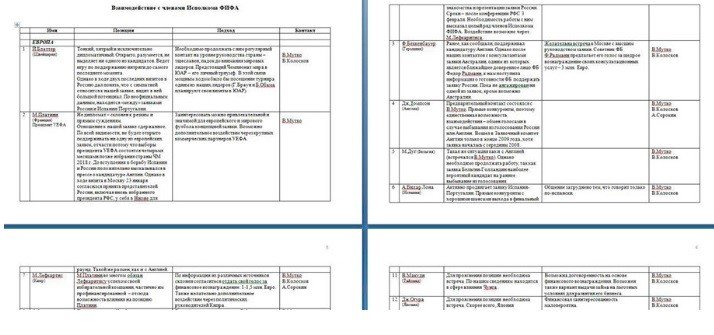
- Reports on committee director meetings

According to information security experts, these new leaks are made up of multiple folders that include various documents, such as files of senior FIFA officials, such as historic former players Franz Beckenbauer and Michel Platini, where instructions for bribing them are detailed.
Fedor Radmann, the German football legend’s adviser, reportedly offered the Russians Beckenbauer’s vote in exchange for a “generous reward”, estimated at more than 3 million Euros. Michel Platini’s file states that it was possible to influence his vote through some of UEFA’s (European football’s governing body) commercial partners, to whom Platini allegedly owed some favors.
Information security experts mention that these files would have been sent via email by a member of the Russia World Cup organizing committee for three senior Russian officials, including Arkady Dvorkovich, chairman of the committee.
On the other hand, Alexei Sorokin, who served as director of the organizing committee of the World Cup in Russia since the nomination more than 10 years ago, has denied the veracity of these leaks, stating that these are fake and meaningless accusations. “The leaked documents mention Russian officials such as Sergei Kapkov, who was not even related to this process; these accusations seem like a set up,” the official added.
It is important to note that the presentation of these documents does not work as evidence that some of the FIFA members have received money in exchange for voting for Russia as the venue for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, as it is only a kind of ‘instructive’ to coerce the organization officials’ decision. However, the issue is not yet closed, so more details could still be leaked about the voting process for the organization of the 2018 and 2022 World Cups.
Information security specialists from the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) highlight the key role that messaging services such as Telegram have played in some cases of information leakage related to multiple cases of corruption, cover-up, among other crimes.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.










