Hostile JavaScript delivered through ads installs ransomware on older Android phones. An ongoing drive-by attack is forcing ransomware onto Android smartphones by exploiting critical vulnerabilities in older versions of Google’s mobile operating system still in use by millions of people, according to research scheduled to be published Monday.
The attack combines exploits for at least two critical vulnerabilities contained in Android versions 4.0 through 4.3, including an exploit known as Towelroot, which gives attackers unfettered “root” access to vulnerable phones. The exploit code appears to borrow heavily from, if not copy outright, some ofthese Android attack scripts, which leaked to the world following the embarrassing breach of Italy-based Hacking Team in July. Additional data indicates devices running Android 4.4 may also be infected, possibly by exploiting a different set of vulnerabilities.
It’s the first time—or at least one of only a handful of times—Android vulnerabilities have been exploited in real-world drive-by attacks. For years, most Android malware has spread by social engineering campaigns that trick a user into installing a malicious app posing as something useful and benign. The drive-by attack—which has been active for at least the past 60 days and was discovered by security firm Blue Coat Systems—is notable because it’s completely stealthy and requires no user interaction. The company’s findings have been published here.
“This looks like a decently sophisticated attack,” said Joshua Drake, vice president for platform research and exploitation at Zimperium. “This attack is powerful because it leverages vulnerabilities in software that’s installed by default to surreptitiously take full control of a victim’s device. As far as I am aware, this attack represents the first in-the-wild drive-by-download attack that exploits a chain of vulnerabilities to target Android users. While this attack uses older vulnerabilities, it represents a change in the tactics used by malicious actors in the Android space.”
Drake’s assessment was based on his review of code that was delivered when a Samsung tablet running Android 4.2.2 in Blue Coat’s lab was infected after viewing a malicious ad delivered over a porn site. Data from Blue Coat logs indicates that at least 224 Android devices running Android 4.x, including 4.4, may have been infected. The handsets were connected to 77 different enterprise networks protected by a Blue Coat security service, so the data likely reflects only a tiny fraction of the total number of infections on the Internet at large.
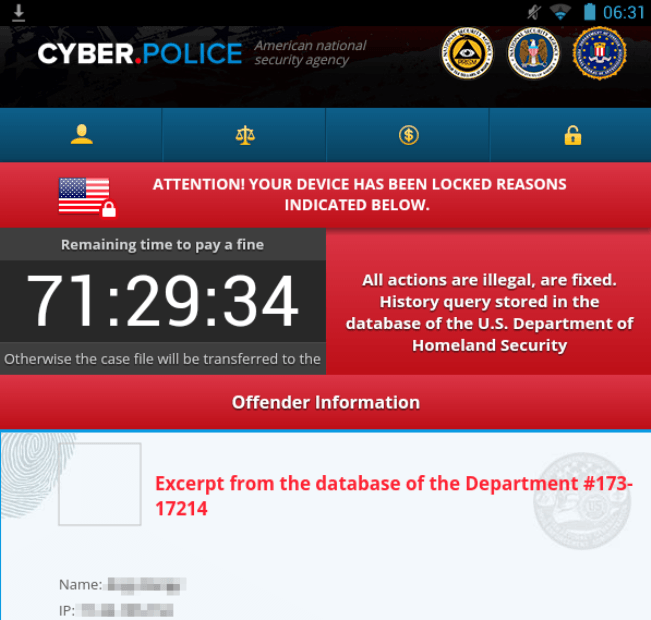
F**K the Cyber.Police
Once the vulnerable Blue Coat tablet visited the booby-trapped webpage, the device was surreptitiously infected with a piece of ransomware called Cyber.Police. The app has been circulating since at least December and threatens legal action for viewing illegal porn unless users pay a fine in the form of one or more $100 Apple iTunes gift cards.
The malicious app puts infected devices into a locked state that prevents them from making or receiving calls or being used for other purposes. The only way Blue Coat researcher Andy Brandt was able to remove the app was to perform a factory reset, but Web searches indicate there may be easier methods involving booting the infected device into safe mode.
During the infection, Brandt captured the traffic that passed between the tablet and the booby-trapped webpage it visited. He provided all of it to Drake for a deeper inspection. Drake’s analysis found that when deobfuscated, the JavaScript served in the attack appeared to be almost identical tothis exploit code leaked from the Hacking Team breach. The Hacking Team JavaScript forces vulnerable Android devices to download and execute any file of an attacker’s choosing. TheExecutable and Linkable Format file served to Brandt’s tablet exploited the Towelroot vulnerability and then executed an Android APK that installed the malicious Cyber.Police app.
The attack used the newly gained root privileges to suppress the usual application permissions dialog that’s supposed to precede installation of an Android app. It also used the elevated privileges to shut down other apps and OS functions and effectively lock the phone.
Towelroot has its genesis in the Linux kernel futex local privilege escalation bug (aka CVE-2014-3153), a bug in the Linux kernel discovered by Comex, a hacker who under the pseudonym Pinkie Pie has also exploited a variety of high-severity vulnerabilities in the Chrome browser. The futex bug allowed unprivileged users or processes to gain unfettered root access rights. Within days fellow hacker George “GeoHot” Hotz had a way Android users could exploit the bug to root their phones to make them do things Google, the hardware manufacturer, or the carrier forbid. Google plugged the Towelroot hole in version 4.4, a version that almost 25 percent of the Android user base has never received.
Crude, yes, but still worth watching
The proficiency of the exploit is in stark contrast to the malicious app itself. Cyber.Police harkens back to an earlier time when ransomware made only vague threats and mostly used easily defeated locking techniques. Unlike newer crypto ransomware, the app doesn’t encrypt files. The use of iTunes gift cards to receive payment is another feature that appears crude when compared with the more current trend of demanding payment in Bitcoin, which is much harder for authorities to trace.
There are other limitations to the attack. For one, even if it uses a separate set of exploits to infect devices running Android 4.4—something that may be possible but has not yet been established—later Android versions are immune. What’s more, all indications so far are that the attacks are spreading only on porn sites and don’t affect mainstream Web properties.
Despite the limitations, there are several reasons the attacks represent a threat that’s worth watching. For one, by Google’s own figures, about 23.5 percent of all Android devices remain vulnerable to the attacks, and if Blue Coat version 4.4 users are indeed susceptible as Blue Coat suspects, the percentage jumps to almost 57 percent. Remember, too, that a sizeable portion of vulnerable handsets will never receive an update.
More broadly, the campaign illustrates that drive-by attacks targeting Android users can be a viable means of infecting people. If criminals can chain together two or more publicly available exploits to install a two-bit ransomware app, there’s no doubt the same technique can be used again, possibly against a wider base of users to install something much more nefarious.

Working as a cyber security solutions architect, Alisa focuses on application and network security. Before joining us she held a cyber security researcher positions within a variety of cyber security start-ups. She also experience in different industry domains like finance, healthcare and consumer products.