Until recently, sample wasn’t detected by any of the top antivirus programs. Researchers have uncovered what appears to be newly developed Mac malware from HackingTeam, a discovery that’s prompting speculation that the disgraced malware-as-a-service provider has reemerged since last July’s hack that spilled gigabytes worth of the group’s private e-mail and source code.
The sample was uploaded on February 4 to the Google-owned VirusTotal scanning service, which at the timeshowed it wasn’t detected by any of the major antivirus programs. (Ahead of this report on Monday, it was detected by 10 of 56 AV services.) A technical analysis published Monday morning by SentinelOne security researcher Pedro Vilaça showed that the installer was last updated in October or November, and an embedded encryption key is dated October 16, three months after the HackingTeam compromise.
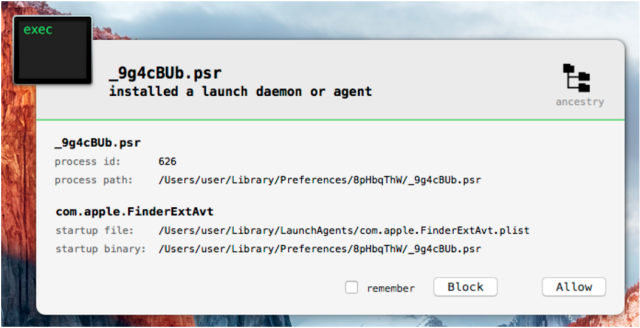
The sample installs a copy of HackingTeam’s signature Remote Code Systems compromise platform, leading Vilaça to conclude that the outfit’s comeback mostly relies on old, largely unexceptional source code, despite the group vowing in July that it would return with new code.
“HackingTeam is still alive and kicking but they are still the same crap morons as the e-mail leaks have show us,” Vilaça wrote. “If you are new to OS X malware reverse engineering, it’s a nice sample to practice with. I got my main questions answered so for me there’s nothing else interesting about this. After the leak I totally forgot about these guys :-).”
Patrick Wardle, a Mac security expert at Synack, has also examined the sample and says that while it appears to install a new version of the old HackingTeam implant, it uses several advanced tricks to evade detection and analysis. For one, it uses Apple’s native encryption scheme to protect the contents of the binary file, making it the first malicious implant installer Wardle has ever seen to do so. Wardle was nonetheless able to break the encryption because Apple uses a static hard-coded key—”ourhardworkbythesewordsguardedpleasedontsteal(c)AppleC”—that has long been known to reverse engineering experts. Even then, he found that the installer was “packed” in a digital wrapper that also limited the types of reverse engineering and analysis he wanted to perform.
The sample still leaves many questions unanswered. For example, it’s not clear how the malware gets installed. One possibility is that targets are tricked into believing that the file installs a benign application. Another possibility is that it’s bundled with an exploit that surreptitiously executes the installer. People who want to know if a Mac is infected should check for a file named Bs-V7qIU.cYL, which is dropped into the ~/Library/Preferences/8pHbqThW/ directory.
Vilaça said he can’t conclusively determine that the new sample is the work of HackingTeam. Since the 400 gigabytes of data that was obtained in the July breach included the Remote Code Systems source code, it’s possible that a different person or group recompiled the code and distributed it in the new installer. Still,Vilaça said evidence from the Shodan search service and a scan of the IP address in VirusTotal show that a command and control server referenced in the sample was active as recently as January, suggesting that the new malware is more than a mere hoax.
Source:https://arstechnica.com/

Working as a cyber security solutions architect, Alisa focuses on application and network security. Before joining us she held a cyber security researcher positions within a variety of cyber security start-ups. She also experience in different industry domains like finance, healthcare and consumer products.











