Experts at Symantec have discovered a new variant of the Chikdos DDoS-Trojan that is targeting MySQL servers worldwide.
There is a malware in the wild that abuses MySQL Servers for DDoS Attacks, the experts named it Chikdos. The threat was detected for the first time by the Polland CERT and according to the experts it has been around since 2013. Chikdos is a DDoS Trojan that is able to infect both Linux and Windows machines to use them to launch DDoS attacks.
“It seems that the bot was created for the sole purpose of performing DDoS attacks. This means that the attackers were interested only in infecting machines which have a significant network bandwidth, e.g. servers. This also probably is the reason why there are two versions of the bot – Linux operating systems are a popular choice for server machines.
Below are the SHA-256 hashes of the analyzed samples.” states the report published by the CERT Poland.
Now researchers at Symantec have detected a new version of the Chikdos malware that presents many similarities with older versions except for its ability to target specific MySQL servers. The choice of MySQL servers as targets of the attacks is not surprising, such kind of machine is very popular and usually they have large bandwidth that can be exploited to launch DDoS attacks.
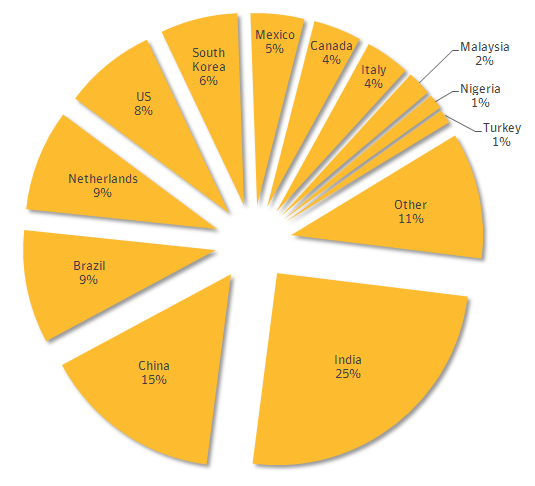
Most of the attacks observed by Symantec have compromised servers are in India, China, Brazil and the Netherlands.
The experts explained that the attacks against MySQL servers start with the injection of malicious user-defined function (UDF) that download the download the other components of the Chikdos Trojan from hardcoded URLs. In some circumstances, the downloader also adds a new user account to the machine.
“We’ve discovered malware that targeted MySQL servers to make them conduct distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against other websites. The attackers initially injected a malicious user-defined function (Downloader.Chikdos) into servers in order to compromise them with the Trojan.Chikdos.A DDoS malware”reported Symantec.
“Our analysis found that the compromised servers were being used to launch DDoS attacks against a Chinese IP address and a US hosting provider.”
The user-defined functions are subroutines composed of more Transact-SQL statements that can be used to encapsulate code for reuse, they typically allow to extend the functionality of a MySQL server.
Despite the user-defined functions are usually injected through via SQL injection attacks, in the case analyzed by Symantec the experts have no clear idea of the infection process. Possible scenarios see the use of automated scanning or a malware to compromise the servers and install the UDF.
As a mitigation strategy, the experts suggest avoiding, where possible, to run SQL servers with administrator privileges and as usual let me remind you to patch applications that rely on the SQL servers.
“To protect against these types of attacks, SQL servers should not be run with administrator privileges where possible. Applications that use the SQL server should be patched regularly and follow good programming practices to mitigate SQL injection vulnerabilities. Check for the presence of new user accounts and ensure that remote access services are configured securely,” suggests Symantec.
Source: Securityaffairs.co

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.











